Student Experiences of the Leaving Certificate Applied Programme
Student Experiences of the Leaving Certificate Applied Programme
Student Experiences of the Leaving Certificate Applied Programme
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
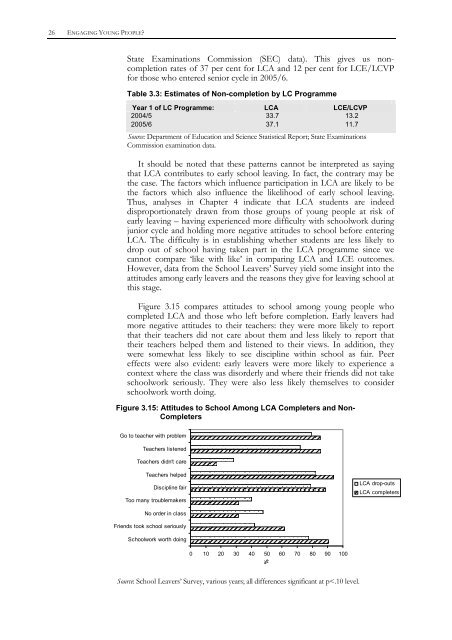
26 ENGAGING YOUNG PEOPLE?State Examinations Commission (SEC) data). This gives us noncompletionrates <strong>of</strong> 37 per cent for LCA and 12 per cent for LCE/LCVPfor those who entered senior cycle in 2005/6.Table 3.3: Estimates <strong>of</strong> Non-completion by LC <strong>Programme</strong>Year 1 <strong>of</strong> LC <strong>Programme</strong>: LCA LCE/LCVP2004/5 33.7 13.22005/6 37.1 11.7Source: Department <strong>of</strong> Education and Science Statistical Report; State ExaminationsCommission examination data.It should be noted that <strong>the</strong>se patterns cannot be interpreted as sayingthat LCA contributes to early school leaving. In fact, <strong>the</strong> contrary may be<strong>the</strong> case. The factors which influence participation in LCA are likely to be<strong>the</strong> factors which also influence <strong>the</strong> likelihood <strong>of</strong> early school leaving.Thus, analyses in Chapter 4 indicate that LCA students are indeeddisproportionately drawn from those groups <strong>of</strong> young people at risk <strong>of</strong>early leaving – having experienced more difficulty with schoolwork duringjunior cycle and holding more negative attitudes to school before enteringLCA. The difficulty is in establishing whe<strong>the</strong>r students are less likely todrop out <strong>of</strong> school having taken part in <strong>the</strong> LCA programme since wecannot compare ‘like with like’ in comparing LCA and LCE outcomes.However, data from <strong>the</strong> School Leavers’ Survey yield some insight into <strong>the</strong>attitudes among early leavers and <strong>the</strong> reasons <strong>the</strong>y give for leaving school atthis stage.Figure 3.15 compares attitudes to school among young people whocompleted LCA and those who left before completion. Early leavers hadmore negative attitudes to <strong>the</strong>ir teachers: <strong>the</strong>y were more likely to reportthat <strong>the</strong>ir teachers did not care about <strong>the</strong>m and less likely to report that<strong>the</strong>ir teachers helped <strong>the</strong>m and listened to <strong>the</strong>ir views. In addition, <strong>the</strong>ywere somewhat less likely to see discipline within school as fair. Peereffects were also evident: early leavers were more likely to experience acontext where <strong>the</strong> class was disorderly and where <strong>the</strong>ir friends did not takeschoolwork seriously. They were also less likely <strong>the</strong>mselves to considerschoolwork worth doing.Figure 3.15: Attitudes to School Among LCA Completers and Non-CompletersGo to teacher with problemTeachers listenedTeachers didn't careTeachers helpedDiscipline fairToo many troublemakersLCA drop-outsLCA completersNo order in classFriends took school seriouslySchoolwork worth doing0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100%Source: School Leavers’ Survey, various years; all differences significant at p