- Page 2 and 3:
SEER ProgramSelf Instructional Manu
- Page 4 and 5:
CONTENTSBOOK 4: HUMAN ANATOMY AS RE
- Page 6 and 7:
ILLUSTRATIONS(Figures 1-82, cont'd)
- Page 8 and 9:
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTSPortions of Book 4
- Page 11:
SECTIONAOBJECTIVES AND CONTENT OF B
- Page 15:
BSECTIONBTERMS USED TO INDICATE BOD
- Page 18 and 19:
Directional Planes of the BodySagit
- Page 20 and 21:
Relative Positional and Directional
- Page 22 and 23:
Figure 3. ANATOMIC DIVISIONSOF THE
- Page 24 and 25:
Answers to Practical ExerciseNote t
- Page 27:
SECTIONCTHE INTEGUMENTARYSYSTEM19
- Page 30 and 31:
EpidermisThe epidermis (Figure 4A)
- Page 33 and 34:
Q1a. What are the two primary layer
- Page 35:
Epidermis is epithelial tissue deri
- Page 38 and 39:
Answer:Q2The three glands of the sk
- Page 41 and 42:
Q3Q4Accessory skin organs are found
- Page 43 and 44:
Benign TumorsThere is a large group
- Page 45 and 46:
Q5 Match the malignant tumors of th
- Page 47 and 48:
MalignantMelanomaMalignant melanoma
- Page 49:
The description of the level 1 of i
- Page 52 and 53:
Q9"Clark's Classification" of malig
- Page 54 and 55:
Lymphatic Drainage of the SkinThe l
- Page 57 and 58:
Q10Match the regions of the skin on
- Page 59:
SECTIONTHE LYMPHATICDSYSTEM51
- Page 62 and 63:
T-Cells Versus B-CeilsThe two princ
- Page 64 and 65:
Answer:Q1The lymphatic system colle
- Page 66 and 67:
Figures 8A-8B. LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE O
- Page 68 and 69:
Answer:Q3The lymphatic system colle
- Page 70 and 71:
Lymph nodes accomplish two separate
- Page 73 and 74:
Q6The lymph nodes have two main fun
- Page 75 and 76:
SpleenThe spleen, the largest lymph
- Page 77 and 78:
Q9Match each lymphatic organ or tis
- Page 79 and 80:
LymphaticDrainageLymph nodes, most
- Page 81 and 82:
Answer:QllLymphatics tend to parall
- Page 83 and 84:
Q14A general term for lymph nodes l
- Page 85:
Lymph Nodes of the ThoraxThe lymph
- Page 88 and 89:
Answer:Q18Lymph nodes of the thorax
- Page 91 and 92:
Q20Lymph nodes of the abdomen may a
- Page 93:
Lymph Nodes of Upper and Lower Extr
- Page 96 and 97:
Answer:Q22c 1. Popliteal Heela 2. A
- Page 98 and 99:
Hodgkin's disease. The histologic c
- Page 100 and 101:
Answer:Q23Benign tumors of lymphoid
- Page 102 and 103:
Extralymphatic/ExtranodalSitesLymph
- Page 104 and 105:
Answer:Q27Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas m
- Page 106 and 107:
TilE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMIonatod
- Page 108 and 109:
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMFigure 14D. BLOOD
- Page 110 and 111:
Answer:Q1The cardiovascular system
- Page 112 and 113:
The heart lies in a loose-fitting s
- Page 114 and 115:
106
- Page 116 and 117:
Answer:Q5The heart has four chamber
- Page 118 and 119:
Answer:QIODeoxygenated blood from t
- Page 120 and 121:
Portal System (portal circulation)V
- Page 122 and 123:
Answer:QllThe three kinds of blood
- Page 124 and 125:
116
- Page 126 and 127:
Answer:QlgThe three main types of b
- Page 128 and 129:
120
- Page 130 and 131:
Answer:Q18White blood cells which a
- Page 132 and 133:
DEVELOPMENTOF WHITE BLOOD CELLSStem
- Page 134 and 135:
Answer:Q20Malignant diseases of the
- Page 136 and 137:
Answer:Q25b 1. Leukemia An uncontro
- Page 138 and 139:
130
- Page 140 and 141:
132
- Page 142 and 143:
Answer:Q1The parts of the respirato
- Page 144 and 145:
136
- Page 146 and 147:
Answer:Q41. Serves as a passageway
- Page 148 and 149:
140
- Page 150 and 151:
Answer:Q7The pharynx can be divided
- Page 152 and 153:
The larynx can be divided into thre
- Page 154 and 155:
146
- Page 156 and 157:
Answer:Q10The three single cartilag
- Page 158 and 159:
150
- Page 160 and 161:
Answer:Q14The windpipe or trachea s
- Page 162 and 163:
The lungs provide a place where lar
- Page 164 and 165:
Answer:Q16The main bronchus, pulmon
- Page 166 and 167:
Clinical ManifestationsClinical man
- Page 168 and 169:
Answer:Q19The interpleural space ma
- Page 170 and 171:
Answer:Q24_g_ 1. Exchange of oxygen
- Page 172 and 173: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Esophagus-RectumP
- Page 174 and 175: The organs of the digestive system
- Page 176 and 177: Answer:Q1The main organs of the dig
- Page 178 and 179: • Lips. The lips form the upper a
- Page 180 and 181: Answer:Q5The lip consists of an exp
- Page 182 and 183: Malignant TumorsMalignant lesions a
- Page 184 and 185: Answer:Q8The tongue is composed of
- Page 186 and 187: • Gums (gingiva). The gums are fo
- Page 188 and 189: Answer:Qllb__ 1. GumMucosal coverin
- Page 190 and 191: 182
- Page 192 and 193: Answer:Q12The palate is the roof of
- Page 194 and 195: 186
- Page 196 and 197: Answer:Q18The major salivary glands
- Page 198 and 199: 190
- Page 200 and 201: Answer:Q21c 1. Gum Retropharyngeala
- Page 202 and 203: Oropharynx. The air and food passag
- Page 204 and 205: 196
- Page 206 and 207: Answer:Q23Another name for the hypo
- Page 208 and 209: Answer:Q25a__ 1. HypopharynxServes
- Page 210 and 211: Answer:Q28a. Tonsillar pillar - Oro
- Page 212 and 213: Figure 31. MEASUREMENTS OF THE ESOP
- Page 214 and 215: 206
- Page 216 and 217: Answer:Q30The esophagus extends fro
- Page 218 and 219: The medial border of the stomach is
- Page 220 and 221: Q33The stomach lies just below thei
- Page 224 and 225: 216
- Page 226 and 227: Answer:Q38The small intestine is ab
- Page 228 and 229: The large intestine receives the fl
- Page 230 and 231: Malignantand Benign TumorsThe usual
- Page 232 and 233: 224
- Page 234 and 235: Answer:Q41The large intestine is ab
- Page 236 and 237: Answer:Q433. The ileocolic lymph no
- Page 238 and 239: Metastatic tumors involving the liv
- Page 240 and 241: Answer:Q45The most common primary t
- Page 242 and 243: 234
- Page 244 and 245: Answer: 046The function of the gall
- Page 246 and 247: 238
- Page 248 and 249: Answer:Q48.The pancreas plays an im
- Page 250 and 251: Figure 39. PRINCIPAL PARTS OF THE U
- Page 252 and 253: The microscopic structure of the re
- Page 254 and 255: Answer:Q1The urinary system consist
- Page 256 and 257: Figure 41. A NEPHRON_ Otomes_JLus_;
- Page 258 and 259: 250
- Page 260 and 261: Answer:Q4The blood is circulated th
- Page 262 and 263: 254
- Page 264 and 265: Answer:Q8The regional lymph node dr
- Page 266 and 267: 258
- Page 268 and 269: Answer:Q12The tube which carries ur
- Page 270 and 271: URINARY BLADDER, RENAL PELVIS AND U
- Page 272 and 273:
Malignant TumorsBladder cancer is t
- Page 274 and 275:
Answer:Q14The urinary bladder is a
- Page 276 and 277:
Q18Theis a membranous tube which co
- Page 278 and 279:
Answer:Q18The urethra is a membrano
- Page 280 and 281:
Figure 44.FEMALE PELVIS (frontal vi
- Page 282 and 283:
CORPUSUTERII I _ 'PRIMARY] ENDOMETR
- Page 284 and 285:
Answer:Q1The female reproductiveorg
- Page 286 and 287:
• Choriocarcinoma, a highly malig
- Page 288 and 289:
Answer:Q6For corpus uteri you might
- Page 290 and 291:
FallopiantubesThe fallopian tubes,
- Page 292 and 293:
Answer:Q7b 1. Uterus Pear-shaped mu
- Page 294 and 295:
Q8Name the three openings of the ut
- Page 296 and 297:
Answer: 08In naming the three openi
- Page 298 and 299:
Regional Lymph NodesThe regional ly
- Page 300 and 301:
6. Vaginal orifice f. Glands that s
- Page 302 and 303:
Answer:Q14The vagina is situated be
- Page 304 and 305:
296
- Page 306 and 307:
298
- Page 308 and 309:
Answer:Q19The breasts overlie the p
- Page 310 and 311:
A tumor specified as "subareolar" i
- Page 312 and 313:
Answer:Q22One of the first and most
- Page 314 and 315:
306
- Page 316 and 317:
ANSWERS TO REVIEW TESTd 1. Gonads i
- Page 318 and 319:
310
- Page 320 and 321:
Answer:Q25The male gonads consist o
- Page 322 and 323:
314
- Page 324 and 325:
Answer:Q27c 1. Epididymis Tube loca
- Page 326 and 327:
Figure 51. PROSTATE GLAND (frontal
- Page 328 and 329:
Answer:Q29b 1. Prostate Gland which
- Page 330 and 331:
RegionalLymph NodesThe regional lym
- Page 332 and 333:
324
- Page 334 and 335:
Answer:Q30Male hormones are produce
- Page 336 and 337:
Figure 53. ENDOCRINEGLANDS328
- Page 338 and 339:
• Prolactin (luteotrophic hormone
- Page 340 and 341:
Parathyroid GlandThere are four par
- Page 342 and 343:
Thymus GlandThe thymus gland is loc
- Page 344 and 345:
Q2Match the hormone on the left wit
- Page 346 and 347:
Answer:Q1d 1. Hormones Organic secr
- Page 348 and 349:
340
- Page 350 and 351:
Figure 58.AXIAL SKELETONSkuLl.342
- Page 352 and 353:
344
- Page 354 and 355:
Answer:Q1The skeletal system is com
- Page 356 and 357:
348
- Page 358 and 359:
Answer:Q4One characteristic which d
- Page 360 and 361:
352
- Page 362 and 363:
Answer:Q8The purpose of the sesamoi
- Page 364 and 365:
Structure of BoneEach long bone of
- Page 366 and 367:
Answer:QllThe numbered parts of the
- Page 368 and 369:
Facial bones. The facial bones are
- Page 370 and 371:
Figure 65. BONES OF THE THORAX Figu
- Page 372 and 373:
Q17Match the bones on the left with
- Page 374 and 375:
Figure 67. APPENDICULARSKELETON366
- Page 376 and 377:
Malignant TumorsBone is derived fro
- Page 378 and 379:
Q20Sites from which metastases to b
- Page 380 and 381:
Q22Match the description on the lef
- Page 382 and 383:
Answer:Q21c 1. Angiosarcoma A malig
- Page 384 and 385:
Figure 68.MUSCLE TYPES376
- Page 386 and 387:
Figure 69. HISTOLOGICAL COMPARISONS
- Page 388 and 389:
Answer:Q1The three types of muscle
- Page 390 and 391:
382
- Page 392 and 393:
Answer:Q61. True Malignant tumors o
- Page 394 and 395:
• Supinators turn the palm upward
- Page 396 and 397:
Answer:Q8The three general function
- Page 398 and 399:
Answer:Q11Match the muscle groups o
- Page 400 and 401:
392
- Page 402 and 403:
Figure 70.NERVE CELL (neuron)394
- Page 404 and 405:
Answer:Q1The central nervous system
- Page 406 and 407:
Figure 71.CEREBRUMCEREBRUMC_ere_etr
- Page 408 and 409:
400
- Page 410 and 411:
Figure 74 CRANIAL NERVES402
- Page 412 and 413:
MalignantTumorsGliomas are tumors o
- Page 414 and 415:
406
- Page 416 and 417:
Answer:Q6Match each term on the lef
- Page 418 and 419:
410
- Page 420 and 421:
412
- Page 422 and 423:
Answer:Q1The five major sensesof th
- Page 424 and 425:
416
- Page 426 and 427:
Answer:Q3The three layers which com
- Page 428 and 429:
420
- Page 430 and 431:
Answer:Q5The eyeball/s not a solid
- Page 432 and 433:
424
- Page 434 and 435:
Answer:Q8Name the lymph nodes which
- Page 436 and 437:
Figure 80. TONGUE: Areas of tasteUv
- Page 438 and 439:
Answer:QllReceptors for the sense o
- Page 440 and 441:
Malignant TumorsTumors of the nasal
- Page 442 and 443:
Answer:Q13The nasal fossa is divide
- Page 444 and 445:
Regional Lymph NodesThe lymphatics
- Page 446 and 447:
Answer:Q16b 1. External ear Made up
- Page 448 and 449:
440
- Page 450 and 451:
HISTOLOGIC TYPE PRIMARY SITELeukemi
- Page 452 and 453:
444
- Page 454 and 455:
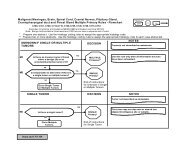
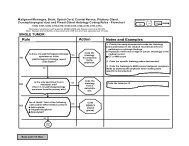
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 456 and 457:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 458 and 459:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 460 and 461:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 462 and 463:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 464 and 465:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 466 and 467:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 468 and 469:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 470 and 471:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 472 and 473:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 474 and 475:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 476 and 477:
DETERMINATION OF SUBSEQUENT PRIMARI
- Page 478 and 479:
470
- Page 480 and 481:
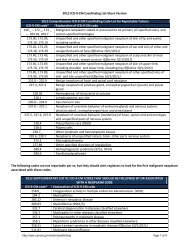
OTHER ICD-O-2 CODES TO BE CONSIDERE
- Page 482 and 483:
474
- Page 484 and 485:
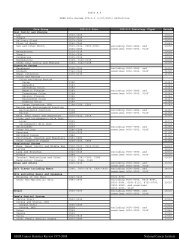
SELECTED BIBLIOGRAPHY (cont'd)Paul,
- Page 486 and 487:
478
- Page 488 and 489:
Adenocarcinoma (continued)Primary s
- Page 490 and 491:
Arteries (see also Vessels) (contin
- Page 492 and 493:
Blood (see also Cardiovascular syst
- Page 494 and 495:
Bone tissue (osseous, vascular tiss
- Page 496 and 497:
Breast (mammary gland) (continued)H
- Page 498 and 499:
Cartilage (nonvascular tissue) (con
- Page 500 and 501:
Cerebrum (forebrain, telencephalon)
- Page 502 and 503:
Cortisol, 329, 333, 336, 338Cortiso
- Page 504 and 505:
Ducts (see also Endocrine system an
- Page 506 and 507:
Estradiol, 281Estrogen-producing ca
- Page 508 and 509:
Follicular adenocarcinoma, 331, 337
- Page 510 and 511:
Glycogen, 229Gonadotrophic hormone
- Page 512 and 513:
Histologic type of cancer, 439-441H
- Page 514 and 515:
Integumentary system (skin) (contin
- Page 516 and 517:
Kidney (see also Urinary system) (c
- Page 518 and 519:
Leukocyte (WBC),Agranular, 119B-Cel
- Page 520 and 521:
Luteal cell, 281Luteinizing hormone
- Page 522 and 523:
Lymph nodes (continued)Perivesical,
- Page 524 and 525:
Lymphoma (continued)Nasopharynx (ph
- Page 526 and 527:
Metastases (continued)Lymph node, 6
- Page 528 and 529:
Muscle (see also Muscular system) (
- Page 530 and 531:
Nervous system, Cranial (continued)
- Page 532 and 533:
Ovary (female gonad), 273, 281,285,
- Page 534 and 535:
Peripheral nervous system, 393, 396
- Page 536 and 537:
Prostate (continued)Urethra (prosta
- Page 538 and 539:
Salivary gland (see also Parotid, S
- Page 540 and 541:
Skull (diploe), 351, 354, 356, 359,
- Page 542 and 543:
Sulcus,Buccal, 178Nasolabial, 39Sup
- Page 544 and 545:
Tibia (shin bone), 351, 369Tumors o
- Page 546 and 547:
Tumor (see also specific histologic
- Page 548 and 549:
Urethra (female, male) (continued)L
- Page 550 and 551:
Vertebral cavity, 10Vertebral colum