Youth Employment Programs - Independent Evaluation Group
Youth Employment Programs - Independent Evaluation Group
Youth Employment Programs - Independent Evaluation Group
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
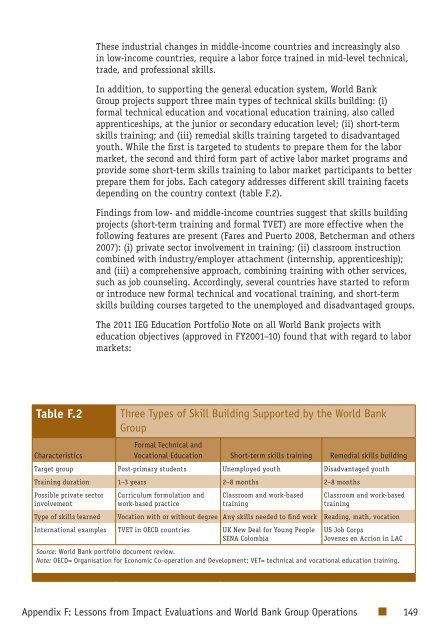
These industrial changes in middle-income countries and increasingly alsoin low-income countries, require a labor force trained in mid-level technical,trade, and professional skills.In addition, to supporting the general education system, World Bank<strong>Group</strong> projects support three main types of technical skills building: (i)formal technical education and vocational education training, also calledapprenticeships, at the junior or secondary education level; (ii) short-termskills training; and (iii) remedial skills training targeted to disadvantagedyouth. While the first is targeted to students to prepare them for the labormarket, the second and third form part of active labor market programs andprovide some short-term skills training to labor market participants to betterprepare them for jobs. Each category addresses different skill training facetsdepending on the country context (table F.2).Findings from low- and middle-income countries suggest that skills buildingprojects (short-term training and formal TVET) are more effective when thefollowing features are present (Fares and Puerto 2008, Betcherman and others2007): (i) private sector involvement in training; (ii) classroom instructioncombined with industry/employer attachment (internship, apprenticeship);and (iii) a comprehensive approach, combining training with other services,such as job counseling. Accordingly, several countries have started to reformor introduce new formal technical and vocational training, and short-termskills building courses targeted to the unemployed and disadvantaged groups.The 2011 IEG Education Portfolio Note on all World Bank projects witheducation objectives (approved in FY2001–10) found that with regard to labormarkets:Table F.2CharacteristicsThree Types of Skill Building Supported by the World Bank<strong>Group</strong>Formal Technical andVocational Education Short-term skills training Remedial skills buildingTarget group Post-primary students Unemployed youth Disadvantaged youthTraining duration 1–3 years 2–8 months 2–8 monthsPossible private sectorinvolvementCurriculum formulation andwork-based practiceClassroom and work-basedtrainingClassroom and work-basedtrainingType of skills learned Vocation with or without degree Any skills needed to find work Reading, math, vocationInternational examples TVET in OECD countries UK New Deal for Young PeopleSENA ColombiaUS Job CorpsJovenes en Accion in LACSource: World Bank portfolio document review.Note: OECD= Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development; VET= technical and vocational education training.Appendix F: Lessons from Impact <strong>Evaluation</strong>s and World Bank <strong>Group</strong> Operations 149