2007_6_Nr6_EEMJ
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Methods and procedures for environmental risk assessment<br />
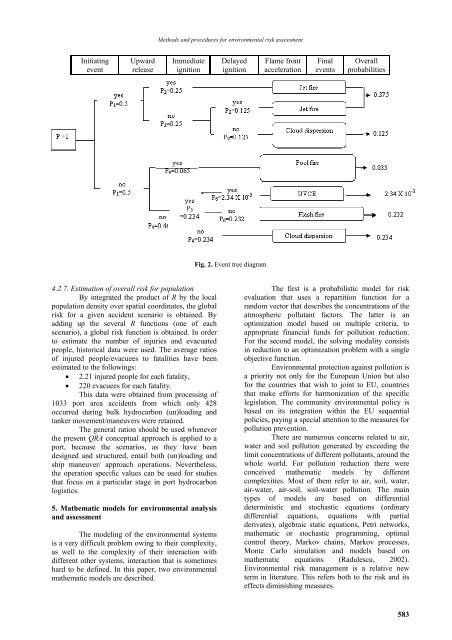
Initiating<br />
event<br />
Upward<br />
release<br />
Immediate<br />
ignition<br />
Delayed<br />
ignition<br />
Flame front<br />
acceleration<br />
Final<br />
events<br />
Overall<br />
probabilities<br />
Fig. 2. Event tree diagram<br />
4.2.7. Estimation of overall risk for population<br />
By integrated the product of R by the local<br />
population density over spatial coordinates, the global<br />
risk for a given accident scenario is obtained. By<br />
adding up the several R functions (one of each<br />
scenario), a global risk function is obtained. In order<br />
to estimate the number of injuries and evacuated<br />
people, historical data were used. The average ratios<br />
of injured people/evacuees to fatalities have been<br />
estimated to the followings:<br />
• 2.21 injured people for each fatality,<br />
• 220 evacuees for each fatality.<br />
This data were obtained from processing of<br />
1033 port area accidents from which only 428<br />
occurred during bulk hydrocarbon (un)loading and<br />
tanker movement/maneuvers were retained.<br />
The general ration should be used whenever<br />
the present QRA conceptual approach is applied to a<br />
port, because the scenarios, as they have been<br />
designed and structured, entail both (un)loading and<br />
ship maneuver/ approach operations. Nevertheless,<br />
the operation specific values can be used for studies<br />
that focus on a particular stage in port hydrocarbon<br />
logistics.<br />
5. Mathematic models for environmental analysis<br />
and assessment<br />
The modeling of the environmental systems<br />
is a very difficult problem owing to their complexity,<br />
as well to the complexity of their interaction with<br />
different other systems, interaction that is sometimes<br />
hard to be defined. In this paper, two environmental<br />
mathematic models are described.<br />
The first is a probabilistic model for risk<br />
evaluation that uses a repartition function for a<br />
random vector that describes the concentrations of the<br />
atmospheric pollutant factors. The latter is an<br />
optimization model based on multiple criteria, to<br />
appropriate financial funds for pollution reduction.<br />
For the second model, the solving modality consists<br />
in reduction to an optimization problem with a single<br />
objective function.<br />
Environmental protection against pollution is<br />
a priority not only for the European Union but also<br />
for the countries that wish to joint to EU, countries<br />
that make efforts for harmonization of the specific<br />
legislation. The community environmental policy is<br />
based on its integration within the EU sequential<br />
policies, paying a special attention to the measures for<br />
pollution prevention.<br />
There are numerous concerns related to air,<br />
water and soil pollution generated by exceeding the<br />
limit concentrations of different pollutants, around the<br />
whole world. For pollution reduction there were<br />
conceived mathematic models by different<br />
complexities. Most of them refer to air, soil, water,<br />
air-water, air-soil, soil-water pollution. The main<br />
types of models are based on differential<br />
deterministic and stochastic equations (ordinary<br />
differential equations, equations with partial<br />
derivates), algebraic static equations, Petri networks,<br />
mathematic or stochastic programming, optimal<br />
control theory, Markov chains, Markov processes,<br />
Monte Carlo simulation and models based on<br />
mathematic equations (Radulescu, 2002).<br />
Environmental risk management is a relative new<br />
term in literature. This refers both to the risk and its<br />
effects diminishing measures.<br />
583