click here to download - UniKL MIMET Official Website
click here to download - UniKL MIMET Official Website
click here to download - UniKL MIMET Official Website
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Diffusion bonding is a joining process between<br />
materials w<strong>here</strong>in the principal mechanism for<br />
joint formation is solid state diffusion. Coales‐<br />
cence of the faying surface is accomplished<br />
through the application of pressure at evevated<br />
temperature. No melting and only limited macro‐<br />
scopic deformation or relative motion of the parts<br />
occurs during bonding. Microscopic deformation<br />
followed by recrystallization occurs. Near the<br />
bond zone, self diffusion in the same materials<br />
and inter diffusion between the materials takes<br />
place simultaneously. New crystalline forms of the<br />
original elements and inter‐metallic compounds<br />
may grow during the process (Paulonis, “Diffusion<br />
Welding and Brazing”).<br />
Other terms which are sometimes used synony‐<br />
mously with diffusion bonding include diffusion<br />
welding, solid state bonding, pressure bonding,<br />
isostatic bonding , and hot press bonding.<br />
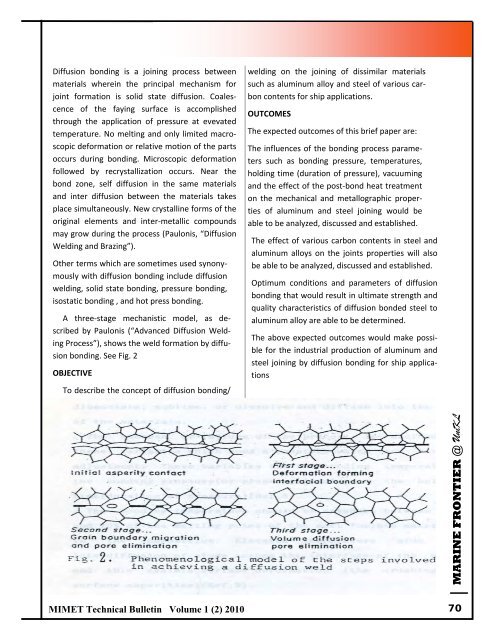
A three‐stage mechanistic model, as de‐<br />
scribed by Paulonis (“Advanced Diffusion Weld‐<br />
ing Process”), shows the weld formation by diffu‐<br />
sion bonding. See Fig. 2<br />
OBJECTIVE<br />
To describe the concept of diffusion bonding/<br />
<strong>MIMET</strong> Technical Bulletin Volume 1 (2) 2010<br />
welding on the joining of dissimilar materials<br />
such as aluminum alloy and steel of various car‐<br />
bon contents for ship applications.<br />
OUTCOMES<br />
The expected outcomes of this brief paper are:<br />
The influences of the bonding process parame‐<br />
ters such as bonding pressure, temperatures,<br />
holding time (duration of pressure), vacuuming<br />
and the effect of the post‐bond heat treatment<br />
on the mechanical and metallographic proper‐<br />
ties of aluminum and steel joining would be<br />
able <strong>to</strong> be analyzed, discussed and established.<br />
The effect of various carbon contents in steel and<br />
aluminum alloys on the joints properties will also<br />
be able <strong>to</strong> be analyzed, discussed and established.<br />
Optimum conditions and parameters of diffusion<br />
bonding that would result in ultimate strength and<br />
quality characteristics of diffusion bonded steel <strong>to</strong><br />
aluminum alloy are able <strong>to</strong> be determined.<br />
The above expected outcomes would make possi‐<br />
ble for the industrial production of aluminum and<br />
steel joining by diffusion bonding for ship applica‐<br />
tions<br />
| MARINE FRONTIER @ <strong>UniKL</strong><br />
70