Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
832 ELIA EFRAIM AND MOSHE EISENBERGER<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
-0.5<br />
-45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45<br />
Ω1,1<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
u<br />
u<br />
u<br />
u<br />
u<br />
u<br />
-45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45<br />
Ω1,2<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
-0.5<br />
u u<br />
u<br />
u u<br />
-1<br />
-45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45<br />
Ω1,3<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
u u<br />
u<br />
u u<br />
u u<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v v<br />
v<br />
v<br />
v v<br />
-0.5<br />
-45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45<br />
Ω1,4<br />
u u<br />
v v<br />
u v<br />
w w<br />
φ<br />
-<br />
w w<br />
w<br />
φ<br />
0.1<br />
0.05<br />
0<br />
-0.05<br />
-0.1<br />
-45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45<br />
ψθ<br />
ψφ<br />
ψ φ<br />
ψ θ<br />
φ φ φ<br />
u wv<br />
-0.2 w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
ψ<br />
φ<br />
φ φ -45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45 ψφ<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
w w<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
-0.1<br />
w<br />
0.1<br />
ψ<br />
θ<br />
φ φ φ<br />
0<br />
w w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
v<br />
-0.1<br />
φ φ φ<br />
-0.2 w w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
u<br />
ψ<br />
φ<br />
φ φ -45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45 φ<br />
w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
w<br />
φ<br />
ψ θ<br />
φ φ φ<br />
w w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
w<br />
ψ<br />
θ<br />
φ φ 0<br />
φ<br />
w w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
-0.2<br />
u vφ<br />
φ φ<br />
-0.4 w w<br />
ψθ ψφ ψ<br />
φ<br />
φ φ -45 -30 -15 0 15 30 45 φ<br />
w<br />
ψθ ψφ<br />
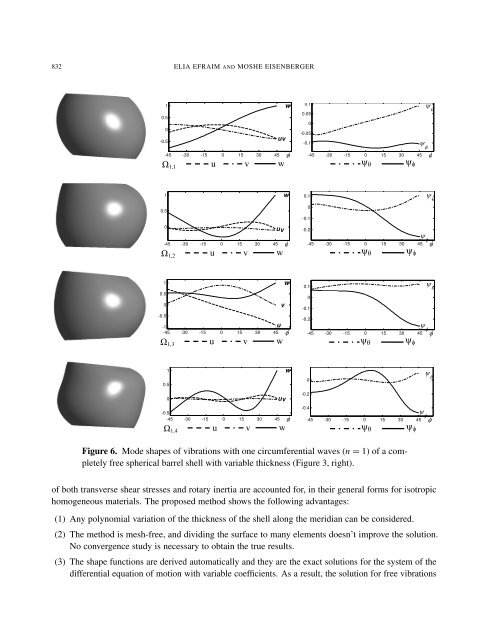
Figure 6. Mode shapes <strong>of</strong> vibrations with one circumferential waves (n = 1) <strong>of</strong> a completely<br />
free spherical barrel shell with variable thickness (Figure 3, right).<br />
<strong>of</strong> both transverse shear stresses <strong>and</strong> rotary inertia are accounted for, in their general forms for isotropic<br />
homogeneous materials. The proposed method shows the following advantages:<br />
(1) Any polynomial variation <strong>of</strong> the thickness <strong>of</strong> the shell along the meridian can be considered.<br />
(2) The method is mesh-free, <strong>and</strong> dividing the surface to many elements doesn’t improve the solution.<br />
No convergence study is necessary to obtain the true results.<br />
(3) The shape functions are derived automatically <strong>and</strong> they are the exact solutions for the system <strong>of</strong> the<br />
differential equation <strong>of</strong> motion with variable coefficients. As a result, the solution for free vibrations<br />
w<br />
ψ