Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures vol. 5 (2010 ... - MSP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PLANAR BEAMS: MIXED VARIATIONAL DERIVATION AND FE SOLUTION 789<br />
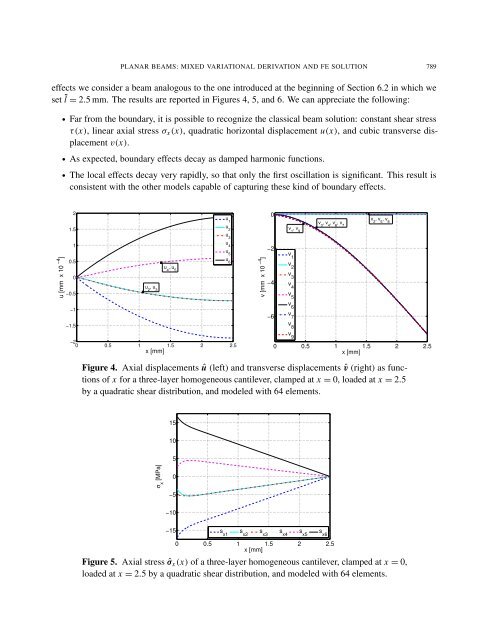
effects we consider a beam analogous to the one introduced at the beginning <strong>of</strong> Section 6.2 in which we<br />
set l = 2.5 mm. The results are reported in Figures 4, 5, <strong>and</strong> 6. We can appreciate the following:<br />
u [mm x 10 −4 ]<br />
• Far from the boundary, it is possible to recognize the classical beam solution: constant shear stress<br />
τ(x), linear axial stress σx(x), quadratic horizontal displacement u(x), <strong>and</strong> cubic transverse displacement<br />
v(x).<br />
• As expected, boundary effects decay as damped harmonic functions.<br />
• The local effects decay very rapidly, so that only the first oscillation is significant. This result is<br />
consistent with the other models capable <strong>of</strong> capturing these kind <strong>of</strong> boundary effects.<br />
2<br />
1.5<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
−0.5<br />
−1<br />
−1.5<br />
u 2 , u 3<br />
u 4 , u 5<br />
−2<br />
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5<br />
x [mm]<br />
u 1<br />
u 2<br />
u 3<br />
u 4<br />
u 5<br />
u 6<br />
v [mm x 10 −4 ]<br />
0<br />
−2<br />
−4<br />
−6<br />
v 1 , v 9<br />
v 1<br />
v 2<br />
v 3<br />
v 4<br />
v 5<br />
v 6<br />
v 7<br />
v 8<br />
v 9<br />
v 3 , v 4 , v 6 , v 7<br />
v 2 , v 5 , v 8<br />
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5<br />
x [mm]<br />
Figure 4. Axial displacements û (left) <strong>and</strong> transverse displacements ˆv (right) as functions<br />
<strong>of</strong> x for a three-layer homogeneous cantilever, clamped at x = 0, loaded at x = 2.5<br />
by a quadratic shear distribution, <strong>and</strong> modeled with 64 elements.<br />
σ x [MPa]<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
−5<br />
−10<br />
−15<br />
s x1<br />
s x2<br />
s x3<br />
s x4<br />
s x5<br />
s x6<br />
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5<br />
x [mm]<br />
Figure 5. Axial stress ˆσx(x) <strong>of</strong> a three-layer homogeneous cantilever, clamped at x = 0,<br />
loaded at x = 2.5 by a quadratic shear distribution, <strong>and</strong> modeled with 64 elements.