Architecture Modeling - SPES 2020
Architecture Modeling - SPES 2020
Architecture Modeling - SPES 2020
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.3.1.1 Ports<br />
<strong>Architecture</strong> <strong>Modeling</strong><br />
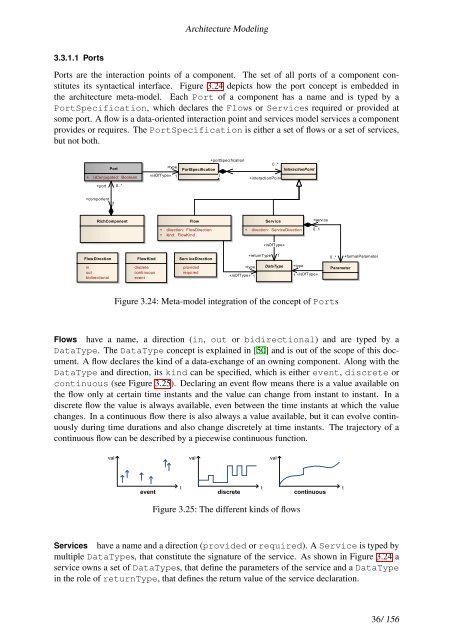
Ports are the interaction points of a component. The set of all ports of a component constitutes<br />
its syntactical interface. Figure 3.24 depicts how the port concept is embedded in<br />
the architecture meta-model. Each Port of a component has a name and is typed by a<br />
PortSpecification, which declares the Flows or Services required or provided at<br />
some port. A flow is a data-oriented interaction point and services model services a component<br />
provides or requires. The PortSpecification is either a set of flows or a set of services,<br />
but not both.<br />
Port<br />
+ isConjugated: Boolean<br />
+port<br />
+component<br />
1<br />
RichComponent<br />
FlowDirection<br />
in<br />
out<br />
bidirectional<br />
0..*<br />
FlowKind<br />
discrete<br />
continuous<br />
event<br />
+portSpecification<br />
+type<br />
PortSpecification<br />
0..*<br />
InteractionPoint<br />
«isOfType» 1<br />
1<br />
+interactionPoint<br />
Flow<br />
+ direction: FlowDirection<br />
+ kind: FlowKind<br />
Serv iceDirection<br />
provided<br />
required<br />
«isOfType» 1<br />
Serv ice<br />
+ direction: ServiceDirection<br />
«isOfType»<br />
+returnType 1<br />
+type<br />
DataType<br />
+type<br />
+service<br />
0..1<br />
1 «isOfType»<br />
Figure 3.24: Meta-model integration of the concept of Ports<br />
0..*<br />
Parameter<br />
+formalParameter<br />
Flows have a name, a direction (in, out or bidirectional) and are typed by a<br />
DataType. The DataType concept is explained in [50] and is out of the scope of this document.<br />
A flow declares the kind of a data-exchange of an owning component. Along with the<br />
DataType and direction, its kind can be specified, which is either event, discrete or<br />
continuous (see Figure 3.25). Declaring an event flow means there is a value available on<br />
the flow only at certain time instants and the value can change from instant to instant. In a<br />
discrete flow the value is always available, even between the time instants at which the value<br />
changes. In a continuous flow there is also always a value available, but it can evolve continuously<br />
during time durations and also change discretely at time instants. The trajectory of a<br />
continuous flow can be described by a piecewise continuous function.<br />
val<br />
event<br />
t<br />
val<br />
discrete<br />
Figure 3.25: The different kinds of flows<br />
t<br />
val<br />
continuous<br />
Services have a name and a direction (provided or required). A Service is typed by<br />
multiple DataTypes, that constitute the signature of the service. As shown in Figure 3.24 a<br />
service owns a set of DataTypes, that define the parameters of the service and a DataType<br />
in the role of returnType, that defines the return value of the service declaration.<br />
t<br />
36/ 156