A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
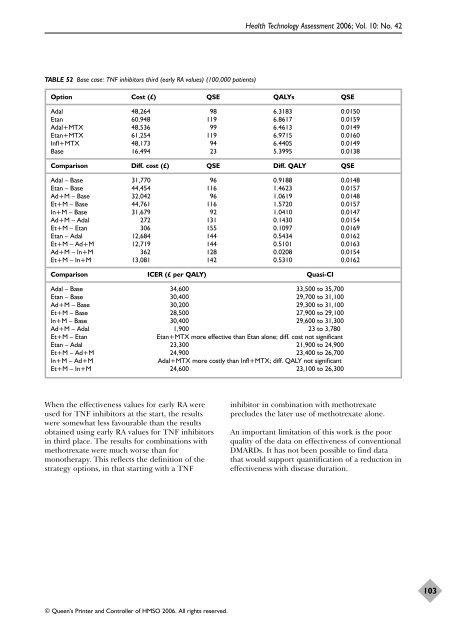
TABLE 52 Base case: TNF inhibitors third (early RA values) (100,000 patients)<br />
© Queen’s Printer and Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO 2006. All rights reserved.<br />
Health Technology Assessment 2006; Vol. 10: No. 42<br />
Option Cost (£) QSE QALYs QSE<br />
Adal 48,264 98 6.3183 0.0150<br />
Etan 60,948 119 6.8617 0.0159<br />
Adal+MTX 48,536 99 6.4613 0.0149<br />
Etan+MTX 61,254 119 6.9715 0.0160<br />
Infl+MTX 48,173 94 6.4405 0.0149<br />
Base 16,494 23 5.3995 0.0138<br />
Comparison Diff. cost (£) QSE Diff. QALY QSE<br />
Adal – Base 31,770 96 0.9188 0.0148<br />
Etan – Base 44,454 116 1.4623 0.0157<br />
Ad+M – Base 32,042 96 1.0619 0.0148<br />
Et+M – Base 44,761 116 1.5720 0.0157<br />
In+M – Base 31,679 92 1.0410 0.0147<br />
Ad+M – Adal 272 131 0.1430 0.0154<br />
Et+M – Etan 306 155 0.1097 0.0169<br />
Etan – Adal 12,684 144 0.5434 0.0162<br />
Et+M – Ad+M 12,719 144 0.5101 0.0163<br />
Ad+M – In+M 362 128 0.0208 0.0154<br />
Et+M – In+M 13,081 142 0.5310 0.0162<br />
Comparison ICER (£ per QALY) Quasi-CI<br />
Adal – Base 34,600 33,500 to 35,700<br />
Etan – Base 30,400 29,700 to 31,100<br />
Ad+M – Base 30,200 29,300 to 31,100<br />
Et+M – Base 28,500 27,900 to 29,100<br />
In+M – Base 30,400 29,600 to 31,300<br />
Ad+M – Adal 1,900 23 to 3,780<br />
Et+M – Etan Etan+MTX more effective than Etan alone; diff. cost not significant<br />
Etan – Adal 23,300 21,900 to 24,900<br />
Et+M – Ad+M 24,900 23,400 to 26,700<br />
In+M – Ad+M Adal+MTX more costly than Infl+MTX; diff. QALY not significant<br />
Et+M – In+M 24,600 23,100 to 26,300<br />
When <strong>the</strong> <strong>effectiveness</strong> values for early RA were<br />
used for TNF inhibitors at <strong>the</strong> start, <strong>the</strong> results<br />
were somewhat less favourable than <strong>the</strong> results<br />
obtained using early RA values for TNF inhibitors<br />
in third place. The results for combinations with<br />
methotrexate were much worse than for<br />
mono<strong>the</strong>rapy. This reflects <strong>the</strong> definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
strategy options, in that starting with a TNF<br />
inhibitor in combination with methotrexate<br />
precludes <strong>the</strong> later use <strong>of</strong> methotrexate alone.<br />
An important limitation <strong>of</strong> this work is <strong>the</strong> poor<br />
quality <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> data on <strong>effectiveness</strong> <strong>of</strong> conventional<br />
DMARDs. It has not been possible to find data<br />
that would support quantification <strong>of</strong> a reduction in<br />
<strong>effectiveness</strong> with disease duration.<br />
103