A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
46<br />
Effectiveness<br />
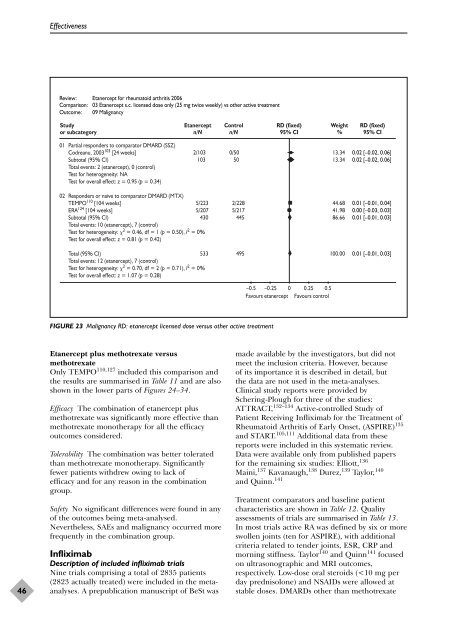
Review: Etanercept for rheumatoid arthritis 2006<br />
Comparison: 03 Etanercept s.c. licensed dose only (25 mg twice weekly) vs o<strong>the</strong>r active treatment<br />
Outcome: 09 Malignancy<br />
Study<br />
or subcategory<br />
01 Partial responders to comparator DMARD (SSZ)<br />
Codreanu, 2003 103 [24 weeks]<br />
Subtotal (95% CI)<br />
Total events: 2 (etanercept), 0 (control)<br />
Test for heterogeneity: NA<br />
Test for overall effect: z = 0.95 (p = 0.34)<br />
Etanercept<br />
n/N<br />
Etanercept plus methotrexate versus<br />
methotrexate<br />
Only TEMPO 110,127 included this comparison and<br />
<strong>the</strong> results are summarised in Table 11 and are also<br />
shown in <strong>the</strong> lower parts <strong>of</strong> Figures 24–34.<br />
Efficacy The combination <strong>of</strong> etanercept plus<br />
methotrexate was significantly more effective than<br />
methotrexate mono<strong>the</strong>rapy for all <strong>the</strong> efficacy<br />
outcomes considered.<br />
Tolerability The combination was better tolerated<br />
than methotrexate mono<strong>the</strong>rapy. Significantly<br />
fewer patients withdrew owing to lack <strong>of</strong><br />
efficacy and for any reason in <strong>the</strong> combination<br />
group.<br />
Safety No significant differences were found in any<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> outcomes being meta-analysed.<br />
Never<strong>the</strong>less, SAEs and malignancy occurred more<br />
frequently in <strong>the</strong> combination group.<br />
Infliximab<br />
Description <strong>of</strong> included infliximab trials<br />
Nine trials comprising a total <strong>of</strong> 2835 patients<br />
(2823 actually treated) were included in <strong>the</strong> metaanalyses.<br />
A prepublication manuscript <strong>of</strong> BeSt was<br />
Control<br />
n/N<br />
2/103 0/50<br />
103 50<br />
02 Responders or naive to comparator DMARD (MTX)<br />
TEMPO110 [104 weeks]<br />
ERA124 [104 weeks]<br />
Subtotal (95% CI)<br />
Total events: 10 (etanercept), 7 (control)<br />
Test for heterogeneity: 2 = 0.46, df = 1 (p = 0.50), I2 5/223 2/228<br />
5/207 5/217<br />
430 445<br />
= 0%<br />
Test for overall effect: z = 0.81 (p = 0.42)<br />
Total (95% CI)<br />
Total events: 12 (etanercept), 7 (control)<br />
Test for heterogeneity: 2 = 0.70, df = 2 (p = 0.71), I2 533 495<br />
= 0%<br />
Test for overall effect: z = 1.07 (p = 0.28)<br />
FIGURE 23 Malignancy RD: etanercept licensed dose versus o<strong>the</strong>r active treatment<br />
RD (fixed)<br />
95% CI<br />
–0.5 –0.25 0 0.25 0.5<br />
Favours etanercept Favours control<br />
Weight<br />
%<br />
13.34<br />
13.34<br />
44.68<br />
41.98<br />
86.66<br />
100.00<br />
RD (fixed)<br />
95% CI<br />
0.02 [–0.02, 0.06]<br />
0.02 [–0.02, 0.06]<br />
0.01 [–0.01, 0.04]<br />
0.00 [–0.03, 0.03]<br />
0.01 [–0.01, 0.03]<br />
0.01 [–0.01, 0.03]<br />
made available by <strong>the</strong> investigators, but did not<br />
meet <strong>the</strong> inclusion criteria. However, because<br />
<strong>of</strong> its importance it is described in detail, but<br />
<strong>the</strong> data are not used in <strong>the</strong> meta-analyses.<br />
Clinical study reports were provided by<br />
Schering-Plough for three <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> studies:<br />
ATTRACT, 132–134 Active-controlled Study <strong>of</strong><br />
Patient Receiving Infliximab for <strong>the</strong> Treatment <strong>of</strong><br />
Rheumatoid Arthritis <strong>of</strong> Early Onset, (ASPIRE) 135<br />
and START. 105,111 Additional data from <strong>the</strong>se<br />
reports were included in this <strong>systematic</strong> <strong>review</strong>.<br />
Data were available only from published papers<br />
for <strong>the</strong> remaining six studies: Elliott, 136<br />
Maini, 137 Kavanaugh, 138 Durez, 139 Taylor, 140<br />
and Quinn. 141<br />
Treatment comparators and baseline patient<br />
characteristics are shown in Table 12. Quality<br />
assessments <strong>of</strong> trials are summarised in Table 13.<br />
In most trials active RA was defined by six or more<br />
swollen joints (ten for ASPIRE), with additional<br />
criteria related to tender joints, ESR, CRP and<br />
morning stiffness. Taylor 140 and Quinn 141 focused<br />
on ultrasonographic and MRI outcomes,<br />
respectively. Low-dose oral steroids (