A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
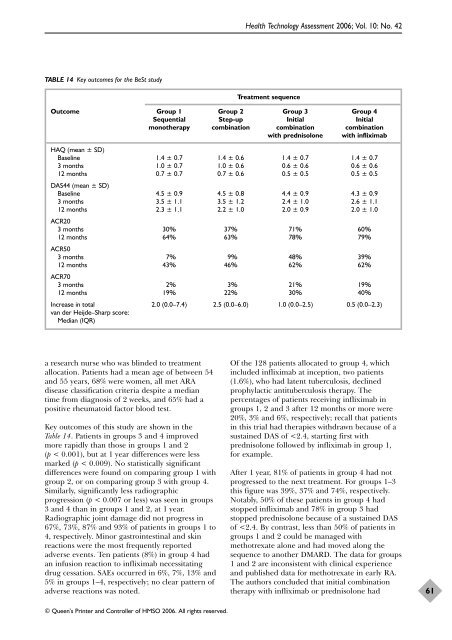
TABLE 14 Key outcomes for <strong>the</strong> BeSt study<br />
a research nurse who was blinded to treatment<br />
allocation. Patients had a mean age <strong>of</strong> between 54<br />
and 55 years, 68% were women, all met ARA<br />
disease classification criteria despite a median<br />
time from diagnosis <strong>of</strong> 2 weeks, and 65% had a<br />
positive rheumatoid factor blood test.<br />
Key outcomes <strong>of</strong> this study are shown in <strong>the</strong><br />
Table 14. Patients in groups 3 and 4 improved<br />
more rapidly than those in groups 1 and 2<br />
(p < 0.001), but at 1 year differences were less<br />
marked (p < 0.009). No statistically significant<br />
differences were found on comparing group 1 with<br />
group 2, or on comparing group 3 with group 4.<br />
Similarly, significantly less radiographic<br />
progression (p < 0.007 or less) was seen in groups<br />
3 and 4 than in groups 1 and 2, at 1 year.<br />
Radiographic joint damage did not progress in<br />
67%, 73%, 87% and 93% <strong>of</strong> patients in groups 1 to<br />
4, respectively. Minor gastrointestinal and skin<br />
reactions were <strong>the</strong> most frequently reported<br />
adverse events. Ten patients (8%) in group 4 had<br />
an infusion reaction to infliximab necessitating<br />
drug cessation. SAEs occurred in 6%, 7%, 13% and<br />
5% in groups 1–4, respectively; no clear pattern <strong>of</strong><br />
adverse reactions was noted.<br />
© Queen’s Printer and Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO 2006. All rights reserved.<br />
Health Technology Assessment 2006; Vol. 10: No. 42<br />
Treatment sequence<br />
Outcome Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4<br />
Sequential Step-up Initial Initial<br />
mono<strong>the</strong>rapy combination combination combination<br />
with prednisolone with infliximab<br />
HAQ (mean ± SD)<br />
Baseline 1.4 ± 0.7 1.4 ± 0.6 1.4 ± 0.7 1.4 ± 0.7<br />
3 months 1.0 ± 0.7 1.0 ± 0.6 0.6 ± 0.6 0.6 ± 0.6<br />
12 months<br />
DAS44 (mean ± SD)<br />
0.7 ± 0.7 0.7 ± 0.6 0.5 ± 0.5 0.5 ± 0.5<br />
Baseline 4.5 ± 0.9 4.5 ± 0.8 4.4 ± 0.9 4.3 ± 0.9<br />
3 months 3.5 ± 1.1 3.5 ± 1.2 2.4 ± 1.0 2.6 ± 1.1<br />
12 months<br />
ACR20<br />
2.3 ± 1.1 2.2 ± 1.0 2.0 ± 0.9 2.0 ± 1.0<br />
3 months 30% 37% 71% 60%<br />
12 months<br />
ACR50<br />
64% 63% 78% 79%<br />
3 months 7% 9% 48% 39%<br />
12 months<br />
ACR70<br />
43% 46% 62% 62%<br />
3 months 2% 3% 21% 19%<br />
12 months 19% 22% 30% 40%<br />
Increase in total 2.0 (0.0–7.4) 2.5 (0.0–6.0) 1.0 (0.0–2.5) 0.5 (0.0–2.3)<br />
van der Heijde–Sharp score:<br />
Median (IQR)<br />
Of <strong>the</strong> 128 patients allocated to group 4, which<br />
included infliximab at inception, two patients<br />
(1.6%), who had latent tuberculosis, declined<br />
prophylactic antituberculosis <strong>the</strong>rapy. The<br />
percentages <strong>of</strong> patients receiving infliximab in<br />
groups 1, 2 and 3 after 12 months or more were<br />
20%, 3% and 6%, respectively; recall that patients<br />
in this trial had <strong>the</strong>rapies withdrawn because <strong>of</strong> a<br />
sustained DAS <strong>of</strong>