Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Environmental</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Accounting</strong><br />
<strong>Procedures</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Principles</strong><br />
∑<br />
<strong>Environmental</strong> Revenues<br />
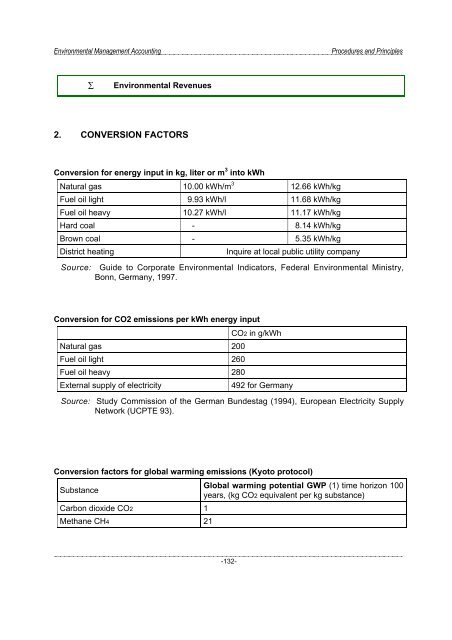
2. CONVERSION FACTORS<br />
Conversion for energy input in kg, liter or m 3 into kWh<br />
Natural gas 10.00 kWh/m 3 12.66 kWh/kg<br />
Fuel oil light 9.93 kWh/l 11.68 kWh/kg<br />
Fuel oil heavy 10.27 kWh/l 11.17 kWh/kg<br />
Hard coal - 8.14 kWh/kg<br />
Brown coal - 5.35 kWh/kg<br />
District heating<br />
Inquire at local public utility company<br />
Source: Guide to Corporate <strong>Environmental</strong> Indicators, Federal <strong>Environmental</strong> Ministry,<br />
Bonn, Germany, 1997.<br />
Conversion for CO2 emissions per kWh energy input<br />
CO2 in g/kWh<br />
Natural gas 200<br />
Fuel oil light 260<br />
Fuel oil heavy 280<br />
External supply of electricity<br />
492 for Germany<br />
Source: Study Commission of the German Bundestag (1994), European Electricity Supply<br />
Network (UCPTE 93).<br />
Conversion factors for global warming emissions (Kyoto protocol)<br />
Substance<br />
Global warming potential GWP (1) time horizon 100<br />
years, (kg CO2 equivalent per kg substance)<br />
Carbon dioxide CO2 1<br />
Methane CH4 21<br />
-132-