Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
Environmental Management Accounting Procedures and Principles
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Environmental</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Accounting</strong><br />
<strong>Procedures</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Principles</strong><br />
It is supplemented with the profit <strong>and</strong> loss accounts, which contain all expenses <strong>and</strong> earnings<br />
incurred in one year. The annex <strong>and</strong> the management report give an explanation of figures, a<br />
description of the assessment methods used <strong>and</strong> an outlook on the economic situation of the<br />
company.<br />
Every accounting transaction is entered into two accounts. The systematic structure of<br />
accounts depends on the so-called chart of accounts, which functions as a requisite<br />
classification <strong>and</strong> organization system for consistency of bookkeeping. The chart of accounts<br />
is structured in the logic of the balance sheet <strong>and</strong> the profit <strong>and</strong> loss accounts. The structure of<br />
the st<strong>and</strong>ard chart of accounts in several continental European countries is shown in figure 13.<br />
However, there is no similar stipulation in other countries.<br />
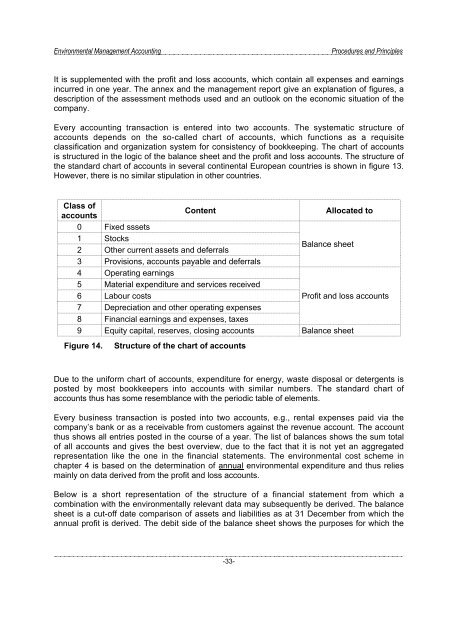
Class of<br />
Content<br />
Allocated to<br />
accounts<br />
0 Fixed sssets<br />
1 Stocks<br />
Balance sheet<br />
2 Other current assets <strong>and</strong> deferrals<br />
3 Provisions, accounts payable <strong>and</strong> deferrals<br />
4 Operating earnings<br />
5 Material expenditure <strong>and</strong> services received<br />
6 Labour costs<br />
Profit <strong>and</strong> loss accounts<br />
7 Depreciation <strong>and</strong> other operating expenses<br />
8 Financial earnings <strong>and</strong> expenses, taxes<br />
9 Equity capital, reserves, closing accounts Balance sheet<br />
Figure 14.<br />
Structure of the chart of accounts<br />
Due to the uniform chart of accounts, expenditure for energy, waste disposal or detergents is<br />
posted by most bookkeepers into accounts with similar numbers. The st<strong>and</strong>ard chart of<br />
accounts thus has some resemblance with the periodic table of elements.<br />
Every business transaction is posted into two accounts, e.g., rental expenses paid via the<br />
company’s bank or as a receivable from customers against the revenue account. The account<br />
thus shows all entries posted in the course of a year. The list of balances shows the sum total<br />
of all accounts <strong>and</strong> gives the best overview, due to the fact that it is not yet an aggregated<br />
representation like the one in the financial statements. The environmental cost scheme in<br />
chapter 4 is based on the determination of annual environmental expenditure <strong>and</strong> thus relies<br />
mainly on data derived from the profit <strong>and</strong> loss accounts.<br />
Below is a short representation of the structure of a financial statement from which a<br />
combination with the environmentally relevant data may subsequently be derived. The balance<br />
sheet is a cut-off date comparison of assets <strong>and</strong> liabilities as at 31 December from which the<br />
annual profit is derived. The debit side of the balance sheet shows the purposes for which the<br />
-33-