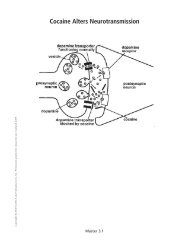
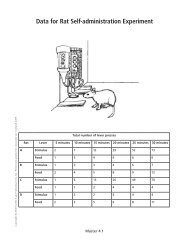
Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Glossary<br />
amplitude: Magnitude, greatness <strong>of</strong> size.<br />
anesthesia: Complete or partial loss <strong>of</strong> sensation,<br />
usually caused by artificially produced unconsciousness.<br />
biological clock: A collection <strong>of</strong> cells that regulates<br />
an overt biological rhythm, such as the<br />
sleep/wake cycle, or some other aspect <strong>of</strong> biological<br />
timing, including reproductive cycles or hibernation.<br />
cataplexy: Sudden muscle weakness associated<br />
with narcolepsy. It is <strong>of</strong>ten triggered by emotions<br />
such as anger, surprise, laughter, and exhilaration.<br />
cerebral cortex: The brain’s outer layer <strong>of</strong> gray<br />
tissue that is responsible for higher nervous<br />
function.<br />
circadian: Exhibiting a periodicity <strong>of</strong> 24 hours.<br />
cyanobacteria: Blue-green algae.<br />
cytokines: Molecules that regulate the functioning<br />
<strong>of</strong> the immune system.<br />
cytoplasm: Protoplasm outside a cell nucleus.<br />
delta waves: Brain waves with a frequency <strong>of</strong> 1 to<br />
3 hertz that emanate from the forward portion <strong>of</strong><br />
the brain during deep sleep in normal adults.<br />
desynchronization: Lack <strong>of</strong> alignment between<br />
external signals and the biological clock.<br />
diurnal: Active or occurring during the daytime;<br />
repeating once each 24 hours.<br />
electroencephalogram (EEG): A measurement<br />
<strong>of</strong> the electrical activity associated with brain<br />
activity.<br />
electromyogram (EMG): A measurement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
electrical activity associated with muscle movements.<br />
electrooculogram (EOG): A measurement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
electrical activity associated with eye movements.<br />
endocrine system: The ductless glands in the<br />
body that secrete hormones.<br />
endogenous rhythms: Rhythms driven by an<br />
internal, self-sustaining biological clock rather<br />
than by signals that are external to the organism<br />
(for example, light).<br />
endothermic animals: Animals that expend<br />
energy to maintain body temperature.<br />
entrain: To reset or align with the biological clock.<br />
enuresis: Bed-wetting.<br />
exacerbate: To aggravate or increase the severity <strong>of</strong>.<br />
exogenous rhythms: A rhythm that is directly regulated<br />
by an external influence, such as an environmental<br />
cue. They are not generated internally<br />
by the organism itself.<br />
follicle stimulating hormone: A hormone produced<br />
in the pituitary gland that stimulates the<br />
growth <strong>of</strong> follicles in the ovary and induces spermatogenesis<br />
in the testes.<br />
frequency: The number <strong>of</strong> times a periodic<br />
process occurs per unit <strong>of</strong> time.<br />
hallucination: A false and distorted perception <strong>of</strong><br />
objects or events.<br />
homeostasis: The ability or tendency <strong>of</strong> an organism<br />
or cell to maintain internal equilibrium by<br />
adjusting its internal processes.<br />
39