Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
Biological - NIH Office of Science Education - National Institutes of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Sleep, Sleep Disorders, and <strong>Biological</strong> Rhythms<br />
homeostatic regulation <strong>of</strong> sleep: Refers to the<br />
neurobiological signals mediating the pressure or<br />
urge to sleep.<br />
hypnagogic hallucination: A “greater-than-lifelike”<br />
dream experience that occurs during sleep.<br />
Hypnagogic hallucinations are sometimes associated<br />
with narcolepsy.<br />
hypnogram: A graphical summary <strong>of</strong> the electrical<br />
activities occurring during a night’s sleep.<br />
hypothalamus: The part <strong>of</strong> the brain that lies<br />
below the thalamus and regulates body temperature<br />
and metabolic processes.<br />
insomnia: Sleeplessness; chronic difficulty with<br />
sleep onset or maintenance <strong>of</strong> sleep, or a perception<br />
<strong>of</strong> nonrefreshing sleep.<br />
luteinizing hormone: A glycoprotein secreted by<br />
the pituitary gland. It stimulates the gonads to<br />
secrete sex steroids.<br />
melatonin: A hormone secreted by the pineal<br />
gland that is derived from the amino acid tryptophan,<br />
which helps synchronize biological clock<br />
neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus.<br />
narcolepsy: A chronic sleep disorder characterized<br />
by excessive and overwhelming daytime<br />
sleepiness (even after adequate nighttime sleep).<br />
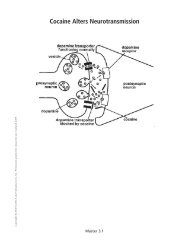
neurotransmitter: A chemical produced by neurons<br />
that carries messages to other neurons.<br />
nocturnal: Relating to or taking place at night.<br />
non–rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep: The<br />
early phase <strong>of</strong> sleep with no rapid eye movement.<br />
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) (sleep apnea syndrome,<br />
sleep-disordered breathing): A disorder<br />
in which breathing is frequently interrupted for<br />
brief intervals during sleep, resulting in intermittent<br />
decreases in blood oxygen levels and transient<br />
arousals from sleep, leading to poor sleep<br />
quality and excessive daytime sleepiness.<br />
oscillation: The state or act <strong>of</strong> swinging back and<br />
forth with a regular, uninterrupted pattern.<br />
parasomnias: Sleep disorders that include sleepwalking,<br />
sleep talking, and sleep terrors.<br />
photoperiod: The light/dark or day/night cycle.<br />
photoreceptor: A molecule or structure that can<br />
detect light.<br />
pons: The brainstem region critical for initiating<br />
REM sleep.<br />
rapid eye movement (REM) sleep: Deep sleep<br />
with rapid eye movements in which dreaming<br />
takes place.<br />
restless legs syndrome: A neurologic movement<br />
disorder that is <strong>of</strong>ten associated with a sleep complaint.<br />
seasonal affective disorder (SAD): A form <strong>of</strong><br />
depression caused by inadequate bright light<br />
reaching the biological clock in the suprachiasmatic<br />
nucleus. Consequently, treatment <strong>of</strong>ten<br />
involves the use <strong>of</strong> light therapy.<br />
sleep hygiene: The collection <strong>of</strong> behaviors and<br />
environmental conditions that influence the<br />
length and quality <strong>of</strong> sleep.<br />
sleep paralysis: The temporary inability to talk or<br />
move when falling asleep or waking up. It occurs<br />
normally during REM sleep.<br />
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN): The part <strong>of</strong> the<br />
brain (in the hypothalamus) that contains the biological<br />
clock.<br />
thalamus: The area <strong>of</strong> the brain that relays sensory<br />
information to the cerebral cortex.<br />
thermoregulation: Maintenance <strong>of</strong> internal<br />
body temperature regardless <strong>of</strong> environmental<br />
temperature.<br />
ubiquitous: Seeming to be everywhere.<br />
ultradian rhythm: A perodicity <strong>of</strong> less than 24<br />
hours.<br />
unihemispheric sleep: A type <strong>of</strong> sleep in which<br />
one side <strong>of</strong> the brain is asleep while the other is<br />
awake. This phenomenon is observed most<br />
notably in birds (like those that make long,<br />
transoceanic flights) and aquatic mammals (like<br />
dolphins and porpoises).<br />
40