- Page 2 and 3:
NationalHuman DevelopmentReport 200
- Page 4 and 5:
ForewordIndonesia has made critical
- Page 6 and 7:
AcknowledgementsThis Report is a re
- Page 8:
AbbreviationsAPBDAPBNASEANBAPPENASB
- Page 11 and 12:
TABLES2.1 - Comparison of per capit
- Page 13 and 14:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARYIndonesiaNational
- Page 15 and 16:
to meet the Millennium Development
- Page 17 and 18:
Chapter 1Indonesia in transition:To
- Page 19 and 20:
The place of human development in I
- Page 21 and 22:
Chapter 2The state of human develop
- Page 23 and 24:
Figure 2.4 - Map of human developme
- Page 25 and 26:
Figure 2.4 - Social indicators, 197
- Page 27 and 28:
of income and corporate taxes has r
- Page 29 and 30:
Figure 2.10 - GDP growth, 1990-2003
- Page 31 and 32:
Table 2.4 - Proportion of total bri
- Page 33 and 34:
In addition, the overall sense of p
- Page 35 and 36:
themselves. On this basis Indonesia
- Page 37 and 38:
Box 3.2 - Pathways to human develop
- Page 39 and 40:
Table 3.3 - Infant mortality rate a
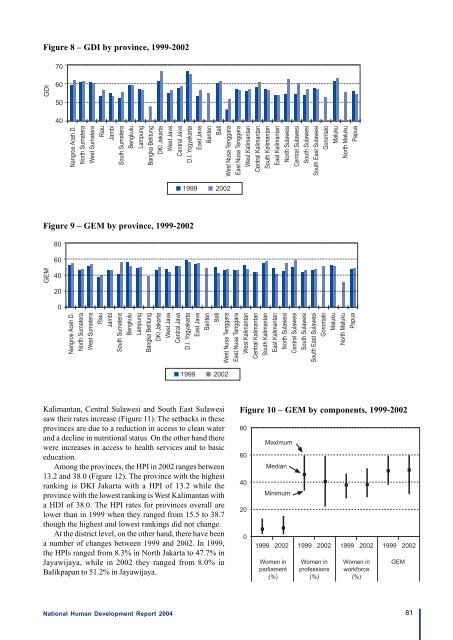
- Page 41 and 42: poor is a clear recognition that de
- Page 43 and 44: educing the infant mortality rate m
- Page 45 and 46: assuming that 1.3 trillion would co
- Page 47 and 48: The national figure would certainly
- Page 49 and 50: expenditure. In practice, it would
- Page 51 and 52: Table 4.2 - Provincial breakdown of
- Page 53 and 54: administration, plus an allowance f
- Page 55 and 56: Figure 4.5 - Ratio of salaries of p
- Page 57 and 58: Appendix to Chapter 4Health and edu
- Page 59 and 60: The third is the ‘Special Fund’
- Page 61 and 62: Chapter 5Rethinking fiscal prioriti
- Page 63 and 64: At the very outset, however, it sho
- Page 65 and 66: enforcement particularly for person
- Page 67 and 68: Another risk from decentralization
- Page 69 and 70: Box 5.2 - Variations in poverty con
- Page 71 and 72: physical security - which contribut
- Page 73 and 74: centre, for example, played a signi
- Page 75 and 76: BibliographyAbidin, A. (2002), 1 st
- Page 77 and 78: LPEM-FEUI (2004), Draft Final Repor
- Page 79 and 80: Subbarao, K., A. Bonnerjee, J. Brai
- Page 81 and 82: HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDICATORS AND IN
- Page 83 and 84: The human development approach brin
- Page 85 and 86: Box 2HDI, HPI-1, GDI and GEMHuman D
- Page 87 and 88: What do the human developmentindice
- Page 89 and 90: Table 1 - Districts making the grea
- Page 91: Table 2 - Districts with the highes
- Page 95 and 96: Figure 12 - HPI by components, 1999
- Page 97 and 98: Technical workshopon human developm
- Page 99 and 100: • The percentage of households wi
- Page 101 and 102: 11 Percentage of people with self-t
- Page 103 and 104: Annex 2N a m esGROUP IIChairperson:
- Page 105 and 106: Changes in names due to the formati
- Page 107 and 108: LampungKab. Lampung Selatan (South
- Page 109 and 110: 1Human Development Index (HDI)by pr
- Page 111 and 112: 3Gender-related Development Index (
- Page 113 and 114: 5Human Poverty Index (HPI)by provin
- Page 115 and 116: ProvinceDistrictLiveexpectancy(year
- Page 117 and 118: ProvinceDistrictLiveexpectancy(year
- Page 119 and 120: ProvinceDistrictLiveexpectancy(year
- Page 121 and 122: ProvinceDistrictLiveexpectancy(year
- Page 123 and 124: ProvinceDistrictLife expectancy(yea
- Page 125 and 126: ProvinceDistrictLife expectancy(yea
- Page 127 and 128: ProvinceDistrictLife expectancy(yea
- Page 129 and 130: 8Gender Development Index (GDI)by d
- Page 131 and 132: ProvinceDistrictProportionof popula
- Page 133 and 134: ProvinceDistrictProportionof popula
- Page 135 and 136: ProvinceDistrictProportionof popula
- Page 137 and 138: 9Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM)by
- Page 139 and 140: ProvinceDistrictParticipationof wom
- Page 141 and 142: ProvinceKabupaten/KotaDistrictParti
- Page 143 and 144:
ProvinceKabupaten/KotaDistrictParti
- Page 145 and 146:
ProvinceDistrictParticipationof wom
- Page 147 and 148:
ProvinceDistrictParticipationof wom
- Page 149 and 150:
ProvinceDistrictParticipationof wom
- Page 151 and 152:
ProvinceDistrictParticipationof wom
- Page 153 and 154:
ProvinceDistrictPeople notexpected
- Page 155 and 156:
ProvinceDistrictPeople notexpected
- Page 157 and 158:
ProvinceDistrictPeople notexpected
- Page 159 and 160:
ProvinceDistrictPeople notexpected
- Page 161 and 162:
ProvinceDistrictInfantmortalityrate
- Page 163 and 164:
ProvinceDistrictInfantmortalityrate
- Page 165 and 166:
ProvinceDistrictInfantmortalityrate
- Page 167 and 168:
ProvinceDistrictInfantmortalityrate
- Page 169 and 170:
ProvinceDistrictSchool Participatio
- Page 171 and 172:
ProvinceDistrictSchool Participatio
- Page 173 and 174:
ProvinceDistrictSchool Participatio
- Page 175 and 176:
ProvinceDistrictSchool Participatio
- Page 177 and 178:
ProvinceDistrictHouseholds withacce
- Page 179 and 180:
ProvinceDistrictHouseholds withacce
- Page 181 and 182:
ProvinceDistrictHouseholds withacce
- Page 183 and 184:
ProvinceDistrictHouseholds withacce
- Page 185 and 186:
ProvinceDistrictReal per capita GRD
- Page 187 and 188:
ProvinceDistrictReal per capita GRD
- Page 189 and 190:
ProvinceDistrictReal per capita GRD
- Page 191 and 192:
ProvinceDistrictReal per capita GRD
- Page 193 and 194:
ProvinceDistrictLabourforceparticip
- Page 195 and 196:
ProvinceDistrictLabourforceparticip
- Page 197 and 198:
ProvinceDistrictLabourforceparticip
- Page 199 and 200:
ProvinceDistrictLabourforceparticip
- Page 201 and 202:
ProvinceDistrictDevelopmentexpendit
- Page 203 and 204:
ProvinceDistrictDevelopmentexpendit
- Page 205 and 206:
ProvinceDistrictDevelopmentexpendit
- Page 207 and 208:
ProvinceDistrictDevelopmentexpendit
- Page 209 and 210:
Computing the indicesThe Human Deve
- Page 211 and 212:
Calculating the HDIThis illustratio
- Page 213 and 214:
Calculating the GDIAs an example, t
- Page 215 and 216:
Definitions of Statistical TermsAcc
- Page 217:
School drop-out rate: the proportio