4(%3)3 - Ecole nationale supérieure de chimie de Montpellier
4(%3)3 - Ecole nationale supérieure de chimie de Montpellier
4(%3)3 - Ecole nationale supérieure de chimie de Montpellier
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
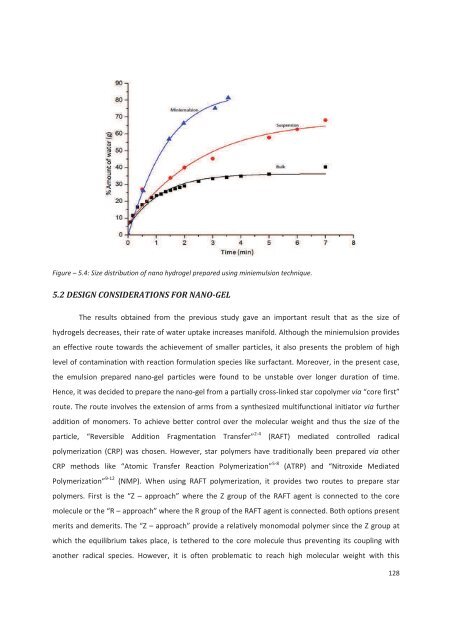
Figure – 5.4: Size distribution of nano hydrogel prepared using miniemulsion technique.5.2 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR NANO-GELThe results obtained from the previous study gave an important result that as the size ofhydrogels <strong>de</strong>creases, their rate of water uptake increases manifold. Although the miniemulsion provi<strong>de</strong>san effective route towards the achievement of smaller particles, it also presents the problem of highlevel of contamination with reaction formulation species like surfactant. Moreover, in the present case,the emulsion prepared nano-gel particles were found to be unstable over longer duration of time.Hence, it was <strong>de</strong>ci<strong>de</strong>d to prepare the nano-gel from a partially cross-linked star copolymer via “core first”route. The route involves the extension of arms from a synthesized multifunctional initiator via furtheraddition of monomers. To achieve better control over the molecular weight and thus the size of theparticle, “Reversible Addition Fragmentation Transfer” 2-4 (RAFT) mediated controlled radicalpolymerization (CRP) was chosen. However, star polymers have traditionally been prepared via otherCRP methods like “Atomic Transfer Reaction Polymerization” 5-8 (ATRP) and “Nitroxi<strong>de</strong> MediatedPolymerization” 9-12 (NMP). When using RAFT polymerization, it provi<strong>de</strong>s two routes to prepare starpolymers. First is the “Z – approach” where the Z group of the RAFT agent is connected to the coremolecule or the “R – approach” where the R group of the RAFT agent is connected. Both options presentmerits and <strong>de</strong>merits. The “Z – approach” provi<strong>de</strong> a relatively monomodal polymer since the Z group atwhich the equilibrium takes place, is tethered to the core molecule thus preventing its coupling withanother radical species. However, it is often problematic to reach high molecular weight with this128