standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
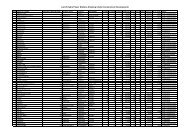
The terms atmospheric overvoltages and switching overvoltages are defined bythemselves. The term temporary overvoltages means overvoltages essentially of powerfrequency or a frequency close to it. Switching overvoltages are of consequence only atlevels above 220 kV and not applicable to system under consideration. The protectionagainst overvoltages is essentially made by Surge diverters (lighting arrestors). Lightningimpulse wave is defined as time in microsecond <strong>for</strong> the wave to reach crest (1.2 microsecond) followed by the time in microsecond <strong>for</strong> the wave to reach half magnitude (50micro second). This has been standardized in the test <strong>for</strong>ms to establish insulation levelon a common basis.2.3.2 Selection of basic Impulse Insulation Level (BIL): Equipment insulation mustwithstand temporary overvoltages and protected against lightning by suitable lightningarrestor. The basic impulse insulation level should be selected which can be protectedwith a suitable lightning protective device. The best protection is provided by moderntype (gapless) lightning arrestors. The spread margin between the BIL and the protectivedevice, allowing <strong>for</strong> manufacturing tolerance, is an economic consideration that mustbalance the chances of insulation failure against the cost of greater insulation strength.When using lightning arrestors the economic factor may be one of greater risk to thearrestor than to the equipment insulation. The arrestor can be applied so that it willprotect the insulation but may under certain extreme conditions, usually unlikely, besubjected to sustained rms temporary over voltages against which it cannot recover.Practice has been to apply arrestors so that they have an rms voltage rating above themaximum possible rms line-to-neutral power frequency voltage under any normal orexpected fault condition with sufficient margin. The BIL of the equipment insulationmust there<strong>for</strong>e be higher than the maximum expected surge voltage across the selectedarrestors selected to withstand highest credible temporary overvotage.2.3.3 Station Design <strong>for</strong> Lightning and Standardisation of Insulation Levels: Stationdesign <strong>for</strong> lightning involves in general, provisions of an adequate insulation level <strong>for</strong> allequipment and protective measures to prevent, as <strong>for</strong> as possible lightning overvoltagesapproaching that level from appearing on station lines or on equipment. These levels aregiven in table 2.1 & 2.2 as per the Indian Standard IS: 2165. In this standard, table 2.1covers the standard insulation levels highest system voltages of 52 kV and below andTable 2.2 <strong>for</strong> highest system voltages of more than 52 kV and less than 300 kV.Table 2.1: Standard Insulation Levels <strong>for</strong> (equipment in range A 1 kV < U m < 52 kV)clause (4) <strong>for</strong> preferred valueHighestVoltage <strong>for</strong>EquipmentU mRated Lightning ImpulseWithstand Voltage (Peak)Rated Short Duration PowerFrequency Withstand Voltage (rms)List 1List2kV kV kV kV3.6 20 40 107.2 40 60 201-3