standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
standards / manuals / guidelines for small hydro development - AHEC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
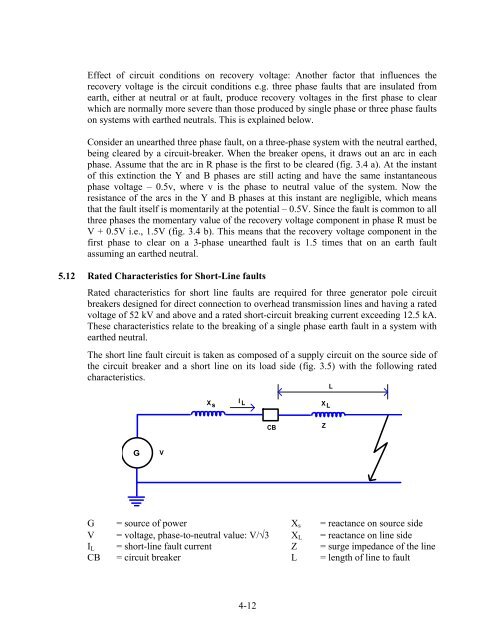
Effect of circuit conditions on recovery voltage: Another factor that influences therecovery voltage is the circuit conditions e.g. three phase faults that are insulated fromearth, either at neutral or at fault, produce recovery voltages in the first phase to clearwhich are normally more severe than those produced by single phase or three phase faultson systems with earthed neutrals. This is explained below.Consider an unearthed three phase fault, on a three-phase system with the neutral earthed,being cleared by a circuit-breaker. When the breaker opens, it draws out an arc in eachphase. Assume that the arc in R phase is the first to be cleared (fig. 3.4 a). At the instantof this extinction the Y and B phases are still acting and have the same instantaneousphase voltage – 0.5v, where v is the phase to neutral value of the system. Now theresistance of the arcs in the Y and B phases at this instant are negligible, which meansthat the fault itself is momentarily at the potential – 0.5V. Since the fault is common to allthree phases the momentary value of the recovery voltage component in phase R must beV + 0.5V i.e., 1.5V (fig. 3.4 b). This means that the recovery voltage component in thefirst phase to clear on a 3-phase unearthed fault is 1.5 times that on an earth faultassuming an earthed neutral.5.12 Rated Characteristics <strong>for</strong> Short-Line faultsRated characteristics <strong>for</strong> short line faults are required <strong>for</strong> three generator pole circuitbreakers designed <strong>for</strong> direct connection to overhead transmission lines and having a ratedvoltage of 52 kV and above and a rated short-circuit breaking current exceeding 12.5 kA.These characteristics relate to the breaking of a single phase earth fault in a system withearthed neutral.The short line fault circuit is taken as composed of a supply circuit on the source side ofthe circuit breaker and a short line on its load side (fig. 3.5) with the following ratedcharacteristics.X sI LX LLCBZGVG = source of power X s = reactance on source sideV = voltage, phase-to-neutral value: V/3 X L = reactance on line sideI L = short-line fault current Z = surge impedance of the lineCB = circuit breaker L = length of line to fault4-12