Skanska Annual Report 2003
Skanska Annual Report 2003
Skanska Annual Report 2003
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
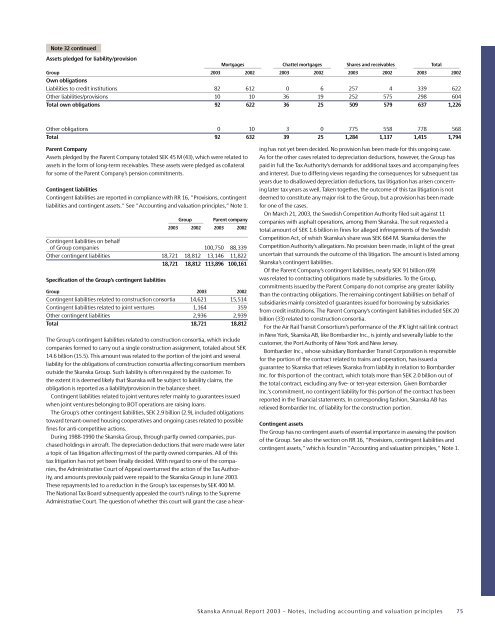
Note 32 continuedAssets pledged for liability/provisionMortgages Chattel mortgages Shares and receivables TotalGroup <strong>2003</strong> 2002 <strong>2003</strong> 2002 <strong>2003</strong> 2002 <strong>2003</strong> 2002Own obligationsLiabilities to credit institutions 82 612 0 6 257 4 339 622Other liabilities/provisions 10 10 36 19 252 575 298 604Total own obligations 92 622 36 25 509 579 637 1,226Other obligations 0 10 3 0 775 558 778 568Total 92 632 39 25 1,284 1,137 1,415 1,794Parent CompanyAssets pledged by the Parent Company totaled SEK 45 M (43), which were related toassets in the form of long-term receivables. These assets were pledged as collateralfor some of the Parent Company’s pension commitments.Contingent liabilitiesContingent liabilities are reported in compliance with RR 16, ”Provisions, contingentliabilities and contingent assets.” See ”Accounting and valuation principles,” Note 1.GroupParent company<strong>2003</strong> 2002 <strong>2003</strong> 2002Contingent liabilities on behalfof Group companies 100,750 88,339Other contingent liabilities 18,721 18,812 13,146 11,82218,721 18,812 113,896 100,161Specification of the Group’s contingent liabilitiesGroup <strong>2003</strong> 2002Contingent liabilities related to construction consortia 14,621 15,514Contingent liabilities related to joint ventures 1,164 359Other contingent liabilities 2,936 2,939Total 18,721 18,812The Group’s contingent liabilities related to construction consortia, which includecompanies formed to carry out a single construction assignment, totaled about SEK14.6 billion (15.5). This amount was related to the portion of the joint and severalliability for the obligations of construction consortia affecting consortium membersoutside the <strong>Skanska</strong> Group. Such liability is often required by the customer. Tothe extent it is deemed likely that <strong>Skanska</strong> will be subject to liability claims, theobligation is reported as a liability/provision in the balance sheet.Contingent liabilities related to joint ventures refer mainly to guarantees issuedwhen joint ventures belonging to BOT operations are raising loans.The Group’s other contingent liabilities, SEK 2.9 billion (2.9), included obligationstoward tenant-owned housing cooperatives and ongoing cases related to possiblefines for anti-competitive actions.During 1988-1990 the <strong>Skanska</strong> Group, through partly owned companies, purchasedholdings in aircraft. The depreciation deductions that were made were latera topic of tax litigation affecting most of the partly owned companies. All of thistax litigation has not yet been finally decided. With regard to one of the companies,the Administrative Court of Appeal overturned the action of the Tax Authority,and amounts previously paid were repaid to the <strong>Skanska</strong> Group in June <strong>2003</strong>.These repayments led to a reduction in the Group’s tax expenses by SEK 400 M.The National Tax Board subsequently appealed the court’s rulings to the SupremeAdministrative Court. The question of whether this court will grant the case a hearinghas not yet been decided. No provision has been made for this ongoing case.As for the other cases related to depreciation deductions, however, the Group haspaid in full the Tax Authority’s demands for additional taxes and accompanying feesand interest. Due to differing views regarding the consequences for subsequent taxyears due to disallowed depreciation deductions, tax litigation has arisen concerninglater tax years as well. Taken together, the outcome of this tax litigation is notdeemed to constitute any major risk to the Group, but a provision has been madefor one of the cases.On March 21, <strong>2003</strong>, the Swedish Competition Authority filed suit against 11companies with asphalt operations, among them <strong>Skanska</strong>. The suit requested atotal amount of SEK 1.6 billion in fines for alleged infringements of the SwedishCompetition Act, of which <strong>Skanska</strong>’s share was SEK 664 M. <strong>Skanska</strong> denies theCompetition Authority’s allegations. No provision been made, in light of the greatuncertain that surrounds the outcome of this litigation. The amount is listed among<strong>Skanska</strong>’s contingent liabilities.Of the Parent Company’s contingent liabilities, nearly SEK 91 billion (69)was related to contracting obligations made by subsidiaries. To the Group,commitments issued by the Parent Company do not comprise any greater liabilitythan the contracting obligations. The remaining contingent liabilities on behalf ofsubsidiaries mainly consisted of guarantees issued for borrowing by subsidiariesfrom credit institutions. The Parent Company’s contingent liabilities included SEK 20billion (33) related to construction consortia.For the Air Rail Transit Consortium’s performance of the JFK light rail link contractin New York, <strong>Skanska</strong> AB, like Bombardier Inc., is jointly and severally liable to thecustomer, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey.Bombardier Inc., whose subsidiary Bombardier Transit Corporation is responsiblefor the portion of the contract related to trains and operation, has issued aguarantee to <strong>Skanska</strong> that relieves <strong>Skanska</strong> from liability in relation to BombardierInc. for this portion of the contract, which totals more than SEK 2.0 billion out ofthe total contract, excluding any five- or ten-year extension. Given BombardierInc.’s commitment, no contingent liability for this portion of the contract has beenreported in the financial statements. In corresponding fashion, <strong>Skanska</strong> AB hasrelieved Bombardier Inc. of liability for the construction portion.Contingent assetsThe Group has no contingent assets of essential importance in asessing the positionof the Group. See also the section on RR 16, ”Provisions, contingent liabilities andcontingent assets,” which is found in ”Accounting and valuation principles,” Note 1.<strong>Skanska</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2003</strong> – Notes, including accounting and valuation principles 75