Download - Volksbank AG
Download - Volksbank AG
Download - Volksbank AG
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
THE BANK FOR CORPORATES<br />
Notes<br />
64<br />
Liquidity risks are similarly assessed which enables the bank to meet its payments when they are due, as well as to procure sufficient<br />
means under the expected conditions if the need occurs. Refinancing within the stipulated time is an essential target to be met in<br />
bank controlling.<br />
(62) CREDIT RISK REPORT. Credit risks imply that debtors are not able to meet their payments. Credit risks comprise non-payment<br />
risks, country risks and default risks whereas the probability of non-payment by a debtor is assessed via different rating schemes.<br />
Therefore, the Bank’s rating system first takes into account the non-payment risk of a debtor. Every borrower is assigned an internal<br />
or external rating. There are eight classes for non-defaulting loans and two classes for defaulting/doubtful loans. The internal<br />
classification corresponds to the standard rating scale of both Moody’s Investors Service and Standard & Poor´s and is carried out in<br />
several steps. Changes in the key balance sheet figures or other information, such as the level of indebtedness in the case of Federal<br />
and local government authorities, can lead to continuous changes in ratings. Ratings must be reassessed at least once a year. Where<br />
an external rating by S & P, Moody’s or Fitch/IBCA is available, the least favourable rating of these agencies is used. Thus, the assets<br />
in the banking book and off-balance-sheet transactions are classified completely by credit standing and collateralisation. Furthermore,<br />
the credit risk is presented as value at risk and the return on risk-adjusted capital (RORAC) is calculated for individual asset classes.<br />
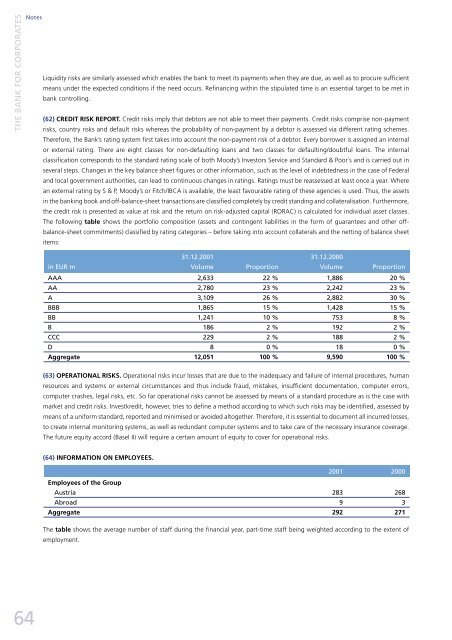
The following table shows the portfolio composition (assets and contingent liabilities in the form of guarantees and other offbalance-sheet<br />
commitments) classified by rating categories – before taking into account collaterals and the netting of balance sheet<br />
items:<br />
31.12.2001 31.12.2000<br />
in EUR m Volume Proportion Volume Proportion<br />
AAA 2,633 22 % 1,886 20 %<br />
AA 2,780 23 % 2,242 23 %<br />
A 3,109 26 % 2,882 30 %<br />
BBB 1,865 15 % 1,428 15 %<br />
BB 1,241 10 % 753 8 %<br />
B 186 2 % 192 2 %<br />
CCC 229 2 % 188 2 %<br />
D 8 0 % 18 0 %<br />
Aggregate 12,051 100 % 9,590 100 %<br />
(63) OPERATIONAL RISKS. Operational risks incur losses that are due to the inadequacy and failure of internal procedures, human<br />
resources and systems or external circumstances and thus include fraud, mistakes, insufficient documentation, computer errors,<br />
computer crashes, legal risks, etc. So far operational risks cannot be assessed by means of a standard procedure as is the case with<br />
market and credit risks. Investkredit, however, tries to define a method according to which such risks may be identified, assessed by<br />
means of a uniform standard, reported and minimised or avoided altogether. Therefore, it is essential to document all incurred losses,<br />
to create internal monitoring systems, as well as redundant computer systems and to take care of the necessary insurance coverage.<br />
The future equity accord (Basel II) will require a certain amount of equity to cover for operational risks.<br />
(64) INFORMATION ON EMPLOYEES.<br />
2001 2000<br />
Employees of the Group<br />
Austria 283 268<br />
Abroad 9 3<br />
Aggregate 292 271<br />
The table shows the average number of staff during the financial year, part-time staff being weighted according to the extent of<br />
employment.