Insomnia Insomnia
Insomnia Insomnia
Insomnia Insomnia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Insomnia</strong> in Psychiatric Disorders 137<br />
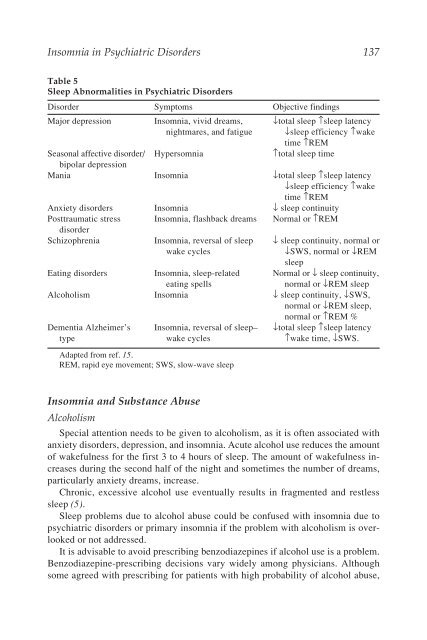
Table 5<br />
Sleep Abnormalities in Psychiatric Disorders<br />
Disorder Symptoms Objective findings<br />
Major depression <strong>Insomnia</strong>, vivid dreams, ↓total sleep ↑sleep latency<br />
nightmares, and fatigue ↓sleep efficiency ↑wake<br />
time ↑REM<br />
Seasonal affective disorder/<br />
bipolar depression<br />
Hypersomnia ↑total sleep time<br />
Mania <strong>Insomnia</strong> ↓total sleep ↑sleep latency<br />
↓sleep efficiency ↑wake<br />
time ↑REM<br />
Anxiety disorders <strong>Insomnia</strong> ↓ sleep continuity<br />
Posttraumatic stress<br />
disorder<br />
<strong>Insomnia</strong>, flashback dreams Normal or ↑REM<br />
Schizophrenia <strong>Insomnia</strong>, reversal of sleep ↓ sleep continuity, normal or<br />
wake cycles ↓SWS, normal or ↓REM<br />
sleep<br />
Eating disorders <strong>Insomnia</strong>, sleep-related Normal or ↓ sleep continuity,<br />
eating spells normal or ↓REM sleep<br />
Alcoholism <strong>Insomnia</strong> ↓ sleep continuity, ↓SWS,<br />
normal or ↓REM sleep,<br />
normal or ↑REM %<br />
Dementia Alzheimer’s <strong>Insomnia</strong>, reversal of sleep– ↓total sleep ↑sleep latency<br />
type wake cycles ↑wake time, ↓SWS.<br />
Adapted from ref. 15.<br />
REM, rapid eye movement; SWS, slow-wave sleep<br />
<strong>Insomnia</strong> and Substance Abuse<br />
Alcoholism<br />
Special attention needs to be given to alcoholism, as it is often associated with<br />
anxiety disorders, depression, and insomnia. Acute alcohol use reduces the amount<br />
of wakefulness for the first 3 to 4 hours of sleep. The amount of wakefulness increases<br />
during the second half of the night and sometimes the number of dreams,<br />
particularly anxiety dreams, increase.<br />
Chronic, excessive alcohol use eventually results in fragmented and restless<br />
sleep (5).<br />
Sleep problems due to alcohol abuse could be confused with insomnia due to<br />
psychiatric disorders or primary insomnia if the problem with alcoholism is overlooked<br />
or not addressed.<br />
It is advisable to avoid prescribing benzodiazepines if alcohol use is a problem.<br />
Benzodiazepine-prescribing decisions vary widely among physicians. Although<br />
some agreed with prescribing for patients with high probability of alcohol abuse,