Breedte geneesmiddelenpakket - Index of
Breedte geneesmiddelenpakket - Index of
Breedte geneesmiddelenpakket - Index of
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
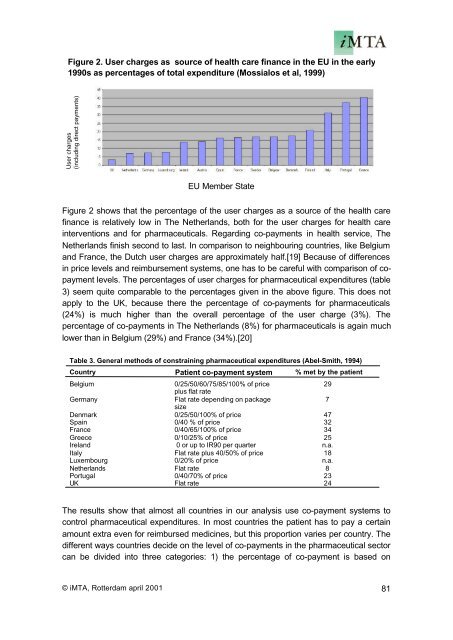
Figure 2. User charges as source <strong>of</strong> health care finance in the EU in the early<br />
1990s as percentages <strong>of</strong> total expenditure (Mossialos et al, 1999)<br />
User charges<br />
(including direct payments)<br />
EU Member State<br />
Figure 2 shows that the percentage <strong>of</strong> the user charges as a source <strong>of</strong> the health care<br />
finance is relatively low in The Netherlands, both for the user charges for health care<br />
interventions and for pharmaceuticals. Regarding co-payments in health service, The<br />
Netherlands finish second to last. In comparison to neighbouring countries, like Belgium<br />
and France, the Dutch user charges are approximately half.[19] Because <strong>of</strong> differences<br />
in price levels and reimbursement systems, one has to be careful with comparison <strong>of</strong> copayment<br />
levels. The percentages <strong>of</strong> user charges for pharmaceutical expenditures (table<br />
3) seem quite comparable to the percentages given in the above figure. This does not<br />
apply to the UK, because there the percentage <strong>of</strong> co-payments for pharmaceuticals<br />
(24%) is much higher than the overall percentage <strong>of</strong> the user charge (3%). The<br />
percentage <strong>of</strong> co-payments in The Netherlands (8%) for pharmaceuticals is again much<br />
lower than in Belgium (29%) and France (34%).[20]<br />
Table 3. General methods <strong>of</strong> constraining pharmaceutical expenditures (Abel-Smith, 1994)<br />
Country Patient co-payment system % met by the patient<br />
Belgium 0/25/50/60/75/85/100% <strong>of</strong> price<br />
plus flat rate<br />
29<br />
Germany Flat rate depending on package<br />
size<br />
7<br />
Denmark 0/25/50/100% <strong>of</strong> price 47<br />
Spain 0/40 % <strong>of</strong> price 32<br />
France 0/40/65/100% <strong>of</strong> price 34<br />
Greece 0/10/25% <strong>of</strong> price 25<br />
Ireland 0 or up to IR90 per quarter n.a.<br />
Italy Flat rate plus 40/50% <strong>of</strong> price 18<br />
Luxembourg 0/20% <strong>of</strong> price n.a.<br />
Netherlands Flat rate 8<br />
Portugal 0/40/70% <strong>of</strong> price 23<br />
UK Flat rate 24<br />
The results show that almost all countries in our analysis use co-payment systems to<br />
control pharmaceutical expenditures. In most countries the patient has to pay a certain<br />
amount extra even for reimbursed medicines, but this proportion varies per country. The<br />
different ways countries decide on the level <strong>of</strong> co-payments in the pharmaceutical sector<br />
can be divided into three categories: 1) the percentage <strong>of</strong> co-payment is based on<br />
© iMTA, Rotterdam april 2001 81