download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.1. TROPOSPHERIC RESEARCH GROUP 19<br />
2.1.1 Halogen oxide and sulphur dioxide emission of volcanoes<br />
Participating scientist Nicole Bobrowski<br />
Abstract A novel instrument, the ’Mini-MAX-DOAS’ was applied to study reactive halogen and<br />
sulphur emissions of several volcanoes. The study was focussed on the determination of SO2 and BrO<br />
concentrations, but also ClO and OClO could be detected for the first time in a volcanic plume. The<br />
chemistry of volcanic plumes can give insights into volcanic processes, which could help to improve the<br />
forecast of volcanic eruptions and is also of atmospheric relevance as the volcanic source of aerosols<br />
and trace gases can have significant climatic impact.<br />
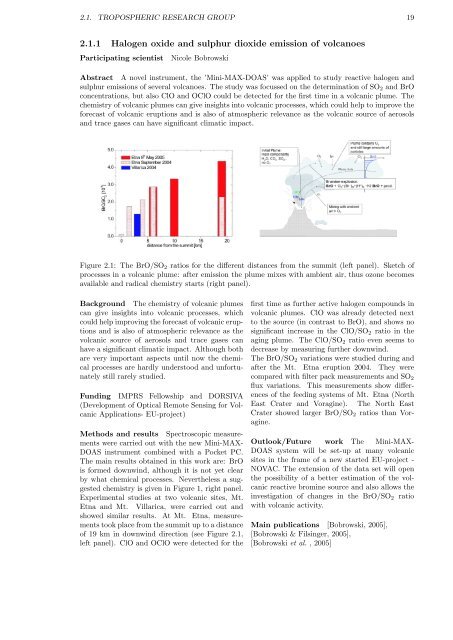
Figure 2.1: The BrO/SO2 ratios for the different distances from the summit (left panel). Sketch of<br />
processes in a volcanic plume: after emission the plume mixes with ambient air, thus ozone becomes<br />
available and radical chemistry starts (right panel).<br />
Background The chemistry of volcanic plumes<br />
can give insights into volcanic processes, which<br />
could help improving the forecast of volcanic eruptions<br />
and is also of atmospheric relevance as the<br />
volcanic source of aerosols and trace gases can<br />
have a significant climatic impact. Although both<br />
are very important aspects until now the chemical<br />
processes are hardly understood and unfortunately<br />
still rarely studied.<br />
Funding IMPRS Fellowship and DORSIVA<br />
(Development of Optical Remote Sensing for Volcanic<br />
Applications- EU-project)<br />
Methods and results Spectroscopic measurements<br />
were carried out with the new Mini-MAX-<br />
DOAS instrument combined with a Pocket PC.<br />
The main results obtained in this work are: BrO<br />
is formed downwind, although it is not yet clear<br />
by what chemical processes. Nevertheless a suggested<br />
chemistry is given in Figure 1, right panel.<br />
Experimental studies at two volcanic sites, Mt.<br />
Etna and Mt. Villarica, were carried out and<br />
showed similar results. At Mt. Etna, measurements<br />
took place from the summit up to a distance<br />
of 19 km in downwind direction (see Figure 2.1,<br />
left panel). ClO and OClO were detected for the<br />
first time as further active halogen compounds in<br />
volcanic plumes. ClO was already detected next<br />
to the source (in contrast to BrO), and shows no<br />
significant increase in the ClO/SO2 ratio in the<br />
aging plume. The ClO/SO2 ratio even seems to<br />
decrease by measuring further downwind.<br />
The BrO/SO2 variations were studied during and<br />
after the Mt. Etna eruption 2004. They were<br />
compared with filter pack measurements and SO2<br />
flux variations. This measurements show differences<br />
of the feeding systems of Mt. Etna (North<br />
East Crater and Voragine). The North East<br />
Crater showed larger BrO/SO2 ratios than Voragine.<br />
Outlook/Future work The Mini-MAX-<br />
DOAS system will be set-up at many volcanic<br />
sites in the frame of a new started EU-project -<br />
NOVAC. The extension of the data set will open<br />
the possibility of a better estimation of the volcanic<br />
reactive bromine source and also allows the<br />
investigation of changes in the BrO/SO2 ratio<br />
with volcanic activity.<br />
Main publications [Bobrowski, 2005],<br />
[Bobrowski & Filsinger, 2005],<br />
[Bobrowski et al. , 2005]