download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.5. SATELLITE GROUP 79<br />
2.5.8 Analysis of global long-term tropospheric and stratospheric BrO<br />
from GOME measurements<br />
Participating scientist Jens Hollwedel, Thomas Wagner, Roland von Glasow, Lars Kaleschke 2 ,<br />
William Simpson 3 , Ulrich Platt ( 2 University of Bremen, 3 University of Alaska)<br />
Abstract BrO leads to ozone depletion, both in the stratosphere and troposphere. The global<br />
distribution and yearly cycle of stratospheric and tropospheric BrO has been analysed. Transport<br />
events and an increase in tropospheric source strength have been discussed.<br />
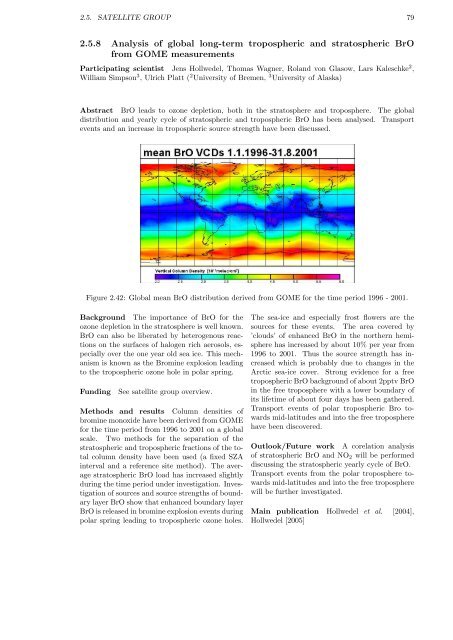
Figure 2.42: Global mean BrO distribution derived from GOME for the time period 1996 - 2001.<br />
Background The importance of BrO for the<br />
ozone depletion in the stratosphere is well known.<br />
BrO can also be liberated by heterogenous reactions<br />
on the surfaces of halogen rich aerosols, especially<br />
over the one year old sea ice. This mechanism<br />
is known as the Bromine explosion leading<br />
to the tropospheric ozone hole in polar spring.<br />
Funding See satellite group overview.<br />
Methods and results Column densities of<br />
bromine monoxide have been derived from GOME<br />
for the time period from 1996 to 2001 on a global<br />
scale. Two methods for the separation of the<br />
stratospheric and tropospheric fractions of the total<br />
column density have been used (a fixed SZA<br />
interval and a reference site method). The average<br />
stratospheric BrO load has increased slightly<br />
during the time period under investigation. Investigation<br />
of sources and source strengths of boundary<br />
layer BrO show that enhanced boundary layer<br />
BrO is released in bromine explosion events during<br />
polar spring leading to tropospheric ozone holes.<br />
The sea-ice and especially frost flowers are the<br />
sources for these events. The area covered by<br />
’clouds’ of enhanced BrO in the northern hemisphere<br />
has increased by about 10% per year from<br />
1996 to 2001. Thus the source strength has increased<br />
which is probably due to changes in the<br />
Arctic sea-ice cover. Strong evidence for a free<br />
tropospheric BrO background of about 2pptv BrO<br />
in the free troposphere with a lower boundary of<br />
its lifetime of about four days has been gathered.<br />
Transport events of polar tropospheric Bro towards<br />
mid-latitudes and into the free troposphere<br />
have been discovered.<br />
Outlook/Future work A corelation analysis<br />
of stratospheric BrO and NO2 will be performed<br />
discussing the stratospheric yearly cycle of BrO.<br />
Transport events from the polar troposphere towards<br />
mid-latitudes and into the free troposphere<br />
will be further investigated.<br />
Main publication Hollwedel et al. [2004],<br />
Hollwedel [2005]