download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.5. SATELLITE GROUP 75<br />
2.5.4 Retrieval of methane from SCIAMACHY onboard ENVISAT<br />
Participating scientist Christian Frankenberg, Ulrich Platt, Thomas Wagner<br />
Abstract SCIAMACHY onboard ENVISAT features three near infrared spectrometers and thereby<br />
enables the retrieval of atmospheric methane with high sensitivity to the lowermost atmospheric layers.<br />
Using concurent retrievals of carbon dioxide and the application of atmospheric models, precise maps<br />
of the global distribution of column averaged methane mixing ratios are derived.<br />
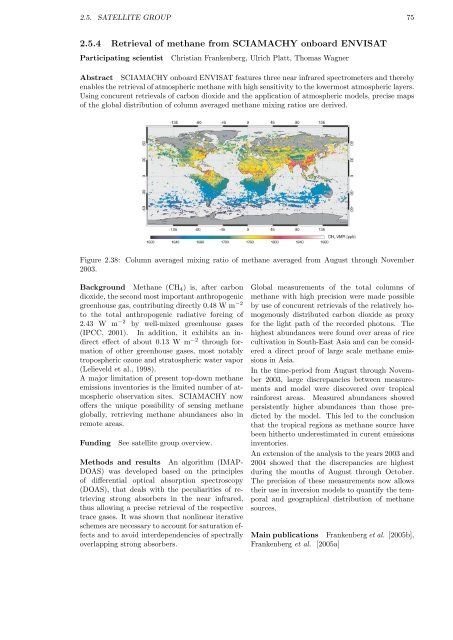
Figure 2.38: Column averaged mixing ratio of methane averaged from August through November<br />
2003.<br />
Background Methane (CH4) is, after carbon<br />
dioxide, the second most important anthropogenic<br />
greenhouse gas, contributing directly 0.48 W m −2<br />
to the total anthropogenic radiative forcing of<br />
2.43 W m −2 by well-mixed greenhouse gases<br />
(IPCC, 2001). In addition, it exhibits an indirect<br />
effect of about 0.13 W m −2 through formation<br />
of other greenhouse gases, most notably<br />
tropospheric ozone and stratospheric water vapor<br />
(Lelieveld et al., 1998).<br />
A major limitation of present top-down methane<br />
emissions inventories is the limited number of atmospheric<br />
observation sites. SCIAMACHY now<br />
offers the unique possibility of sensing methane<br />
globally, retrieving methane abundances also in<br />
remote areas.<br />
Funding See satellite group overview.<br />
Methods and results An algorithm (IMAP-<br />
DOAS) was developed based on the principles<br />
of differential optical absorption spectroscopy<br />
(DOAS), that deals with the peculiarities of retrieving<br />
strong absorbers in the near infrared,<br />
thus allowing a precise retrieval of the respective<br />
trace gases. It was shown that nonlinear iterative<br />
schemes are necessary to account for saturation effects<br />
and to avoid interdependencies of spectrally<br />
overlapping strong absorbers.<br />
Global measurements of the total columns of<br />
methane with high precision were made possible<br />
by use of concurent retrievals of the relatively homogenously<br />
distributed carbon dioxide as proxy<br />
for the light path of the recorded photons. The<br />
highest abundances were found over areas of rice<br />
cultivation in South-East Asia and can be considered<br />
a direct proof of large scale methane emissions<br />
in Asia.<br />
In the time-period from August through November<br />
2003, large discrepancies between measurements<br />
and model were discovered over tropical<br />
rainforest areas. Measured abundances showed<br />
persistently higher abundances than those predicted<br />
by the model. This led to the conclusion<br />
that the tropical regions as methane source have<br />
been hitherto underestimated in curent emissions<br />
inventories.<br />
An extension of the analysis to the years 2003 and<br />
2004 showed that the discrepancies are highest<br />
during the months of August through October.<br />
The precision of these measurements now allows<br />
their use in inversion models to quantify the temporal<br />
and geographical distribution of methane<br />
sources.<br />
Main publications Frankenberg et al. [2005b],<br />
Frankenberg et al. [2005a]