download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
38 CHAPTER 2. ATMOSPHERE AND REMOTE SENSING<br />
2.2.1 Investigation of Inorganic Stratospheric Bromine<br />
Participating scientists Dorf, M., A. Butz, F. Weidner, and K. Pfeilsticker<br />
Abstract Balloon-borne DOAS (Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy) bromine monoxide<br />
(BrO) measurements and model simulations are used to investigate the inorganic stratospheric<br />
bromine chemistry and to validate BrO limb profiling from the new SCIAMACHY instrument on the<br />
European Envisat (ENVIronment SATellite) satellite.<br />
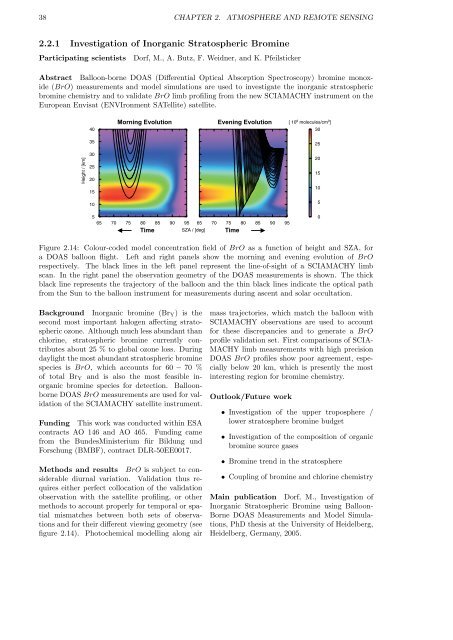
Morning Evolution Evening Evolution<br />
Time Time<br />
Figure 2.14: Colour-coded model concentration field of BrO as a function of height and SZA, for<br />
a DOAS balloon flight. Left and right panels show the morning and evening evolution of BrO<br />
respectively. The black lines in the left panel represent the line-of-sight of a SCIAMACHY limb<br />
scan. In the right panel the observation geometry of the DOAS measurements is shown. The thick<br />
black line represents the trajectory of the balloon and the thin black lines indicate the optical path<br />
from the Sun to the balloon instrument for measurements during ascent and solar occultation.<br />
Background Inorganic bromine (BrY) is the<br />
second most important halogen affecting stratospheric<br />
ozone. Although much less abundant than<br />
chlorine, stratospheric bromine currently contributes<br />
about 25 % to global ozone loss. During<br />
daylight the most abundant stratospheric bromine<br />
species is BrO, which accounts for 60 − 70 %<br />
of total BrY and is also the most feasible inorganic<br />
bromine species for detection. Balloonborne<br />
DOAS BrO measurements are used for validation<br />
of the SCIAMACHY satellite instrument.<br />
Funding This work was conducted within ESA<br />
contracts AO 146 and AO 465. Funding came<br />
from the BundesMinisterium <strong>für</strong> Bildung und<br />
Forschung (BMBF), contract DLR-50EE0017.<br />
Methods and results BrO is subject to considerable<br />
diurnal variation. Validation thus requires<br />
either perfect collocation of the validation<br />
observation with the satellite profiling, or other<br />
methods to account properly for temporal or spatial<br />
mismatches between both sets of observations<br />
and for their different viewing geometry (see<br />
figure 2.14). Photochemical modelling along air<br />
mass trajectories, which match the balloon with<br />
SCIAMACHY observations are used to account<br />
for these discrepancies and to generate a BrO<br />
profile validation set. First comparisons of SCIA-<br />
MACHY limb measurements with high precision<br />
DOAS BrO profiles show poor agreement, especially<br />
below 20 km, which is presently the most<br />
interesting region for bromine chemistry.<br />
Outlook/Future work<br />
• Investigation of the upper troposphere /<br />
lower stratosphere bromine budget<br />
• Investigation of the composition of organic<br />
bromine source gases<br />
• Bromine trend in the stratosphere<br />
• Coupling of bromine and chlorine chemistry<br />
Main publication Dorf, M., Investigation of<br />
Inorganic Stratospheric Bromine using Balloon-<br />
Borne DOAS Measurements and Model Simulations,<br />
PhD thesis at the University of Heidelberg,<br />
Heidelberg, Germany, 2005.