download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
78 CHAPTER 2. ATMOSPHERE AND REMOTE SENSING<br />
2.5.7 Satellite validation using the airborne multi axis DOAS instrument<br />
Participating scientists Klaus-Peter Heue, Thomas Wagner, Andreas Richter 2 , Marco Bruns 2<br />
Ping Wang 2 ( 2 <strong>Institut</strong> <strong>für</strong> Umweltphyisk, <strong>Universität</strong> Bremen)<br />
Abstract The Airborne Multi AXis DOAS instrument designed to separate the tropospheric from<br />
stratospheric absorptions of several Trace gases e.g. NO2. Due to the long range of the aeroplane<br />
it is ideal for validation measurements of tropospheric NO2 observed by the new satellite instrument<br />
SCIAMACHY on ENVISAT.<br />
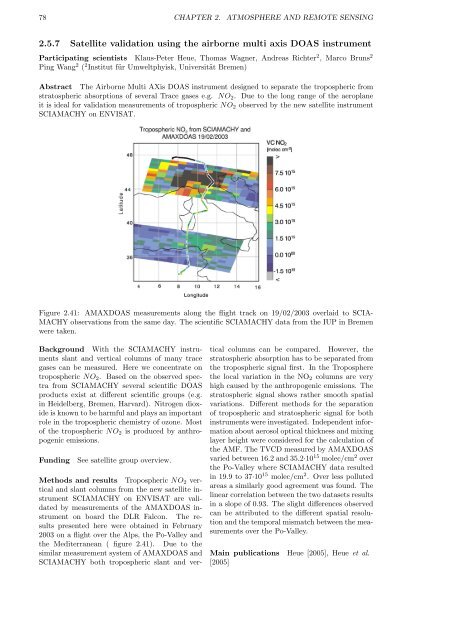
Figure 2.41: AMAXDOAS measurements along the flight track on 19/02/2003 overlaid to SCIA-<br />
MACHY observations from the same day. The scientific SCIAMACHY data from the IUP in Bremen<br />
were taken.<br />
Background With the SCIAMACHY instruments<br />
slant and vertical columns of many trace<br />
gases can be measured. Here we concentrate on<br />
tropospheric NO2. Based on the observed spectra<br />
from SCIAMACHY several scientific DOAS<br />
products exist at different scientific groups (e.g.<br />
in Heidelberg, Bremen, Harvard). Nitrogen dioxide<br />
is known to be harmful and plays an important<br />
role in the tropospheric chemistry of ozone. Most<br />
of the tropospheric NO2 is produced by anthropogenic<br />
emissions.<br />
Funding See satellite group overview.<br />
Methods and results Tropospheric NO2 vertical<br />
and slant columns from the new satellite instrument<br />
SCIAMACHY on ENVISAT are validated<br />
by measurements of the AMAXDOAS instrument<br />
on board the DLR Falcon. The results<br />
presented here were obtained in February<br />
2003 on a flight over the Alps, the Po-Valley and<br />
the Mediterranean ( figure 2.41). Due to the<br />
similar measurement system of AMAXDOAS and<br />
SCIAMACHY both tropospheric slant and ver-<br />
tical columns can be compared. However, the<br />
stratospheric absorption has to be separated from<br />
the tropospheric signal first. In the Troposphere<br />
the local variation in the NO2 columns are very<br />
high caused by the anthropogenic emissions. The<br />
stratospheric signal shows rather smooth spatial<br />
variations. Different methods for the separation<br />
of tropospheric and stratospheric signal for both<br />
instruments were investigated. Independent information<br />
about aerosol optical thickness and mixing<br />
layer height were considered for the calculation of<br />
the AMF. The TVCD measured by AMAXDOAS<br />
varied between 16.2 and 35.2·10 15 molec/cm 2 over<br />
the Po-Valley where SCIAMACHY data resulted<br />
in 19.9 to 37·10 15 molec/cm 2 . Over less polluted<br />
areas a similarly good agreement was found. The<br />
linear correlation between the two datasets results<br />
in a slope of 0.93. The slight differences observed<br />
can be attributed to the different spatial resolution<br />
and the temporal mismatch between the measurements<br />
over the Po-Valley.<br />
Main publications Heue [2005], Heue et al.<br />
[2005]