download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.5. SATELLITE GROUP 87<br />
2.5.16 Analysis of MAXDOAS observations in various observing geometries<br />
Participating scientist Thomas Wagner, Nicole Bobrowski, Barbara Dix, Erna Frins, Ossama<br />
Ibrahim, Roman Sinreich<br />
Abstract MAX-DOAS measurements were caried out at various locations including ship borne<br />
measurements. Sophisticated analysis strategies were developed which can yield vertical profiles not<br />
only of the trace gases of interest, but also of aerosol properties. In addition, a new tomographic<br />
MAX-DOAS technique was developed which allows to determined three-dimensional trace gas fields.<br />
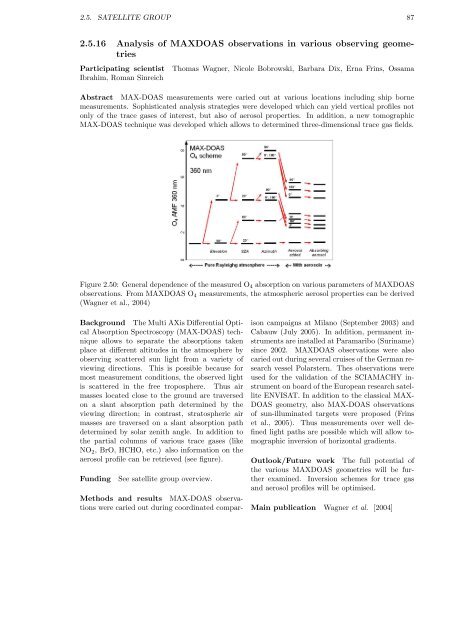
Figure 2.50: General dependence of the measured O4 absorption on various parameters of MAXDOAS<br />
observations. From MAXDOAS O4 measurements, the atmospheric aerosol properties can be derived<br />
(Wagner et al., 2004)<br />
Background The Multi AXis Differential Optical<br />
Absorption Spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) technique<br />
allows to separate the absorptions taken<br />
place at different altitudes in the atmosphere by<br />
observing scattered sun light from a variety of<br />
viewing directions. This is possible because for<br />
most measurement conditions, the observed light<br />
is scattered in the free troposphere. Thus air<br />
masses located close to the ground are traversed<br />
on a slant absorption path determined by the<br />
viewing direction; in contrast, stratospheric air<br />
masses are traversed on a slant absorption path<br />
determined by solar zenith angle. In addition to<br />
the partial columns of various trace gases (like<br />
NO2, BrO, HCHO, etc.) also information on the<br />
aerosol profile can be retrieved (see figure).<br />
Funding See satellite group overview.<br />
Methods and results MAX-DOAS observations<br />
were caried out during coordinated compar-<br />
ison campaigns at Milano (September 2003) and<br />
Cabauw (July 2005). In addition, permanent instruments<br />
are installed at Paramaribo (Suriname)<br />
since 2002. MAXDOAS observations were also<br />
caried out during several cruises of the German research<br />
vessel Polarstern. Thes observations were<br />
used for the validation of the SCIAMACHY instrument<br />
on board of the European research satellite<br />
ENVISAT. In addition to the classical MAX-<br />
DOAS geometry, also MAX-DOAS observations<br />
of sun-illuminated targets were proposed (Frins<br />
et al., 2005). Thus measurements over well defined<br />
light paths are possible which will allow tomographic<br />
inversion of horizontal gradients.<br />
Outlook/Future work The full potential of<br />
the various MAXDOAS geometries will be further<br />
examined. Inversion schemes for trace gas<br />
and aerosol profiles will be optimised.<br />
Main publication Wagner et al. [2004]