download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.1. TROPOSPHERIC RESEARCH GROUP 21<br />
2.1.3 Improvement of the Detection Limit of Active-DOAS-Measurements<br />
by use of fibre coupled light source<br />
Participating scientist André Merten<br />
Abstract Xenon-high-pressure lamps are commonly used in DOAS measurements. Unfortunately<br />
these lamps show strong spectral variability, which determines the minimum detectable optical density.<br />
A combination of a technical solution and a mathematical treatment to reduce the residual structures<br />
and therefore the detection limit was developed.<br />
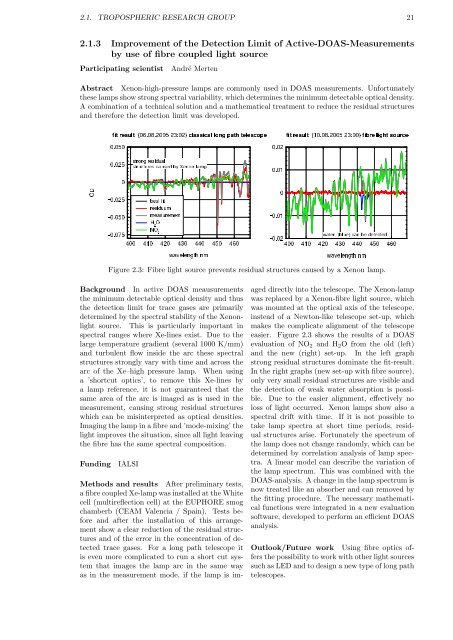
Figure 2.3: Fibre light source prevents residual structures caused by a Xenon lamp.<br />
Background In active DOAS meausurements<br />
the minimum detectable optical density and thus<br />
the detection limit for trace gases are primarily<br />
determined by the spectral stability of the Xenonlight<br />
source. This is particularly important in<br />
spectral ranges where Xe-lines exist. Due to the<br />
large temperature gradient (several 1000 K/mm)<br />
and turbulent flow inside the arc these spectral<br />
structures strongly vary with time and across the<br />
arc of the Xe–high pressure lamp. When using<br />
a ’shortcut optics’, to remove this Xe-lines by<br />
a lamp reference, it is not guaranteed that the<br />
same area of the arc is imaged as is used in the<br />
measurement, causing strong residual structures<br />
which can be misinterpreted as optical densities.<br />
Imaging the lamp in a fibre and ’mode-mixing’ the<br />
light improves the situation, since all light leaving<br />
the fibre has the same spectral composition.<br />
Funding IALSI<br />
Methods and results After preliminary tests,<br />
a fibre coupled Xe-lamp was installed at the White<br />
cell (multireflection cell) at the EUPHORE smog<br />
chamberb (CEAM Valencia / Spain). Tests before<br />
and after the installation of this arrangement<br />
show a clear reduction of the residual structures<br />
and of the error in the concentration of detected<br />
trace gases. For a long path telescope it<br />
is even more complicated to run a short cut system<br />
that images the lamp arc in the same way<br />
as in the measurement mode, if the lamp is im-<br />
aged directly into the telescope. The Xenon-lamp<br />
was replaced by a Xenon-fibre light source, which<br />
was mounted at the optical axis of the telescope,<br />
instead of a Newton-like telescope set-up, which<br />
makes the complicate alignment of the telescope<br />
easier. Figure 2.3 shows the results of a DOAS<br />
evaluation of NO2 and H2O from the old (left)<br />
and the new (right) set-up. In the left graph<br />
strong residual structures dominate the fit-result.<br />
In the right graphs (new set-up with fibre source),<br />
only very small residual structures are visible and<br />
the detection of weak water absorption is possible.<br />
Due to the easier alignment, effectively no<br />
loss of light occurred. Xenon lamps show also a<br />
spectral drift with time. If it is not possible to<br />
take lamp spectra at short time periods, residual<br />
structures arise. Fortunately the spectrum of<br />
the lamp does not change randomly, which can be<br />
determined by correlation analysis of lamp spectra.<br />
A linear model can describe the variation of<br />
the lamp spectrum. This was combined with the<br />
DOAS-analysis. A change in the lamp spectrum is<br />
now treated like an absorber and can removed by<br />
the fitting procedure. The necessary mathematical<br />
functions were integrated in a new evaluation<br />
software, developed to perform an efficient DOAS<br />
analysis.<br />
Outlook/Future work Using fibre optics offers<br />
the possibility to work with other light sources<br />
such as LED and to design a new type of long path<br />
telescopes.