download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2.1. TROPOSPHERIC RESEARCH GROUP 23<br />
2.1.5 Ground based MAX-DOAS measurements<br />
Participating scientists Ossama Ibrahim, Thomas Wagner, Ulrich Platt<br />
Abstract The Multi-axis DOAS technique uses scattered sunlight to obtain information about the<br />
trace gases in the atmosphere by pointing a telescope to different elevation angles and thus receiving<br />
light from different directions. Using Multi-axis DOAS instrument on a stable or movable ground<br />
based platform can also be used to validate DOAS measurements done by satellite instruments.<br />
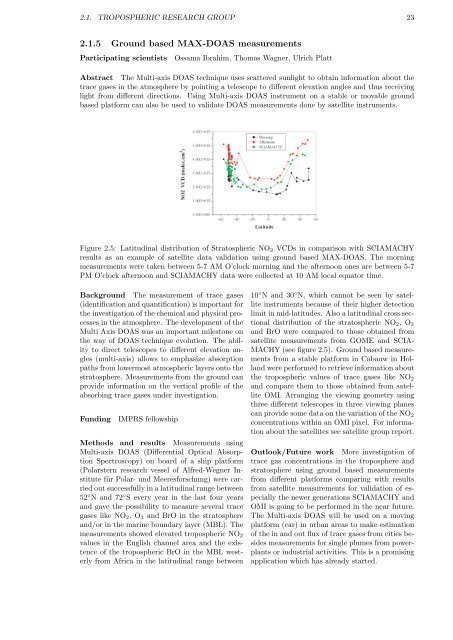
Figure 2.5: Latitudinal distribution of Stratospheric NO2 VCDs in comparison with SCIAMACHY<br />
results as an example of satellite data validation using ground based MAX-DOAS. The morning<br />
measurements were taken between 5-7 AM O’clock morning and the afternoon ones are between 5-7<br />
PM O’clock afternoon and SCIAMACHY data were collected at 10 AM local equator time.<br />
Background The measurement of trace gases<br />
(identification and quantification) is important for<br />
the investigation of the chemical and physical processes<br />
in the atmosphere. The development of the<br />
Multi Axis DOAS was an important milestone on<br />
the way of DOAS technique evolution. The ability<br />
to direct telescopes to different elevation angles<br />
(multi-axis) allows to emphasize absorption<br />
paths from lowermost atmospheric layers onto the<br />
stratosphere. Measurements from the ground can<br />
provide information on the vertical profile of the<br />
absorbing trace gases under investigation.<br />
Funding IMPRS fellowship<br />
Methods and results Measurements using<br />
Multi-axis DOAS (Differential Optical Absorption<br />
Spectroscopy) on board of a ship platform<br />
(Polarstern research vessel of Alfred-Wegner <strong>Institut</strong>e<br />
<strong>für</strong> Polar- und Meeresforschung) were carried<br />
out successfully in a latitudinal range between<br />
52 ◦ N and 72 ◦ S every year in the last four years<br />
and gave the possibility to measure several trace<br />
gases like NO2, O3 and BrO in the stratosphere<br />
and/or in the marine boundary layer (MBL). The<br />
measurements showed elevated tropospheric NO2<br />
values in the English channel area and the existence<br />
of the tropospheric BrO in the MBL westerly<br />
from Africa in the latitudinal range between<br />
10 ◦ N and 30 ◦ N, which cannot be seen by satellite<br />
instruments because of their higher detection<br />
limit in mid-latitudes. Also a latitudinal cross sectional<br />
distribution of the stratospheric NO2, O3<br />
and BrO were compared to those obtained from<br />
satellite measurements from GOME and SCIA-<br />
MACHY (see figure 2.5). Ground based measurements<br />
from a stable platform in Cabauw in Holland<br />
were performed to retrieve information about<br />
the tropospheric values of trace gases like NO2<br />
and compare them to those obtained from satellite<br />
OMI. Arranging the viewing geometry using<br />
three different telescopes in three viewing planes<br />
can provide some data on the variation of the NO2<br />
concentrations within an OMI pixel. For information<br />
about the satellites see satellite group report.<br />
Outlook/Future work More investigation of<br />
trace gas concentrations in the troposphere and<br />
stratosphere using ground based measurements<br />
from different platforms comparing with results<br />
from satellite measurements for validation of especially<br />
the newer generations SCIAMACHY and<br />
OMI is going to be performed in the near future.<br />
The Multi-axis DOAS will be used on a moving<br />
platform (car) in urban areas to make estimation<br />
of the in and out flux of trace gases from cities besides<br />
measurements for single plumes from powerplants<br />
or industrial activities. This is a promising<br />
application which has already started.