download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
download pdf - Institut für Umweltphysik - Ruprecht-Karls-Universität ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
20 CHAPTER 2. ATMOSPHERE AND REMOTE SENSING<br />
2.1.2 Studies of Reactive Halogen Species (RHS) in the Marine and mid-<br />
Latitudinal Boundary Layer by Active Longpath Differential Optical<br />
Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS)<br />
Participating scientist Christina Peters<br />
Abstract Appearance and distribution of a variety of reactive halogen species like BrO, IO, OIO<br />
and I2 in coastal areas was investigated within the framework of this PhD thesis.<br />
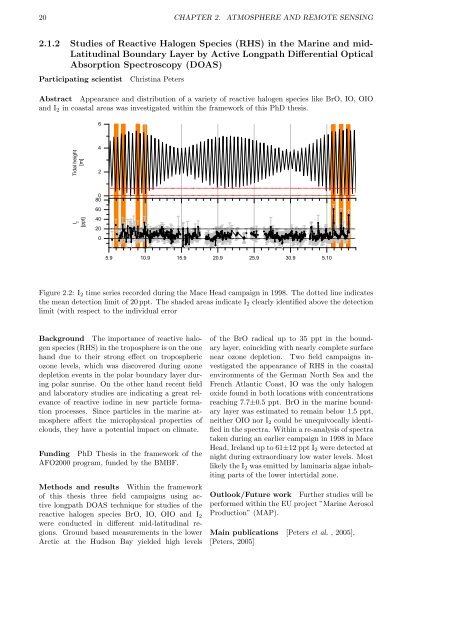
Figure 2.2: I2 time series recorded during the Mace Head campaign in 1998. The dotted line indicates<br />
the mean detection limit of 20 ppt. The shaded areas indicate I2 clearly identified above the detection<br />
limit (with respect to the individual error<br />
Background The importance of reactive halogen<br />
species (RHS) in the troposphere is on the one<br />
hand due to their strong effect on tropospheric<br />
ozone levels, which was discovered during ozone<br />
depletion events in the polar boundary layer during<br />
polar sunrise. On the other hand recent field<br />
and laboratory studies are indicating a great relevance<br />
of reactive iodine in new particle formation<br />
processes. Since particles in the marine atmosphere<br />
affect the microphysical properties of<br />
clouds, they have a potential impact on climate.<br />
Funding PhD Thesis in the framework of the<br />
AFO2000 program, funded by the BMBF.<br />
Methods and results Within the framework<br />
of this thesis three field campaigns using active<br />
longpath DOAS technique for studies of the<br />
reactive halogen species BrO, IO, OIO and I2<br />
were conducted in different mid-latitudinal regions.<br />
Ground based measurements in the lower<br />
Arctic at the Hudson Bay yielded high levels<br />
of the BrO radical up to 35 ppt in the boundary<br />
layer, coinciding with nearly complete surface<br />
near ozone depletion. Two field campaigns investigated<br />
the appearance of RHS in the coastal<br />
environments of the German North Sea and the<br />
French Atlantic Coast, IO was the only halogen<br />
oxide found in both locations with concentrations<br />
reaching 7.7±0.5 ppt. BrO in the marine boundary<br />
layer was estimated to remain below 1.5 ppt,<br />
neither OIO nor I2 could be unequivocally identified<br />
in the spectra. Within a re-analysis of spectra<br />
taken during an earlier campaign in 1998 in Mace<br />
Head, Ireland up to 61±12 ppt I2 were detected at<br />
night during extraordinary low water levels. Most<br />
likely the I2 was emitted by laminaria algae inhabiting<br />
parts of the lower intertidal zone.<br />
Outlook/Future work Further studies will be<br />
performed within the EU project ”Marine Aerosol<br />
Production” (MAP).<br />
Main publications [Peters et al. , 2005],<br />
[Peters, 2005]