- Page 1 and 2:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 De
- Page 3 and 4:
Deutsche Bank The Group at a glance
- Page 5 and 6:
Contents Letter from the Chairman o
- Page 7 and 8:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Le
- Page 9 and 10:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Le
- Page 11 and 12:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Le
- Page 13 and 14:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Gr
- Page 15 and 16:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Re
- Page 17 and 18:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Re
- Page 19 and 20:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Re
- Page 21 and 22:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Re
- Page 23 and 24:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Su
- Page 25 and 26:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 21
- Page 27 and 28:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 01
- Page 29 and 30:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 01
- Page 31 and 32:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 01
- Page 33 and 34:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 01
- Page 35 and 36:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Cl
- Page 37 and 38:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 So
- Page 39 and 40:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Al
- Page 41 and 42:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 43 and 44:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 45 and 46:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 47 and 48:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 49 and 50:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 51 and 52:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 53 and 54:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 55 and 56:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 57 and 58:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 59 and 60:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 61 and 62:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 02
- Page 63 and 64:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 59
- Page 65 and 66:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 St
- Page 67 and 68:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Gr
- Page 69 and 70:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 I
- Page 71 and 72:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Gl
- Page 73 and 74:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 I
- Page 75 and 76:
Deutsche Bank Annual Review 2010 Im
- Page 77 and 78:
Global presence Close to our client
- Page 79 and 80:
The uncertainty of our times remind
- Page 81 and 82:
Deutsche Bank Financial Report 2010
- Page 83 and 84:
Deutsche Bank Content 1 Financial R
- Page 85 and 86:
Management Report and Report of the
- Page 87 and 88:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 89 and 90:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 91 and 92:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 93 and 94:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 95 and 96:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 97 and 98:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 99 and 100:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 101 and 102:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 103 and 104:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 105 and 106:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 107 and 108:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 109 and 110:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 111 and 112:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 113 and 114:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 115 and 116:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 117 and 118:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 119 and 120:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 121 and 122:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 123 and 124:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 125 and 126:
Deutsche Bank Report of the Supervi
- Page 127 and 128:
Deutsche Bank Report of the Supervi
- Page 129 and 130:
Deutsche Bank Report of the Supervi
- Page 131 and 132:
Deutsche Bank Report of the Supervi
- Page 133 and 134:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 135 and 136:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 137 and 138:
Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 139 and 140: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 141 and 142: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 143 and 144: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 145 and 146: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 147 and 148: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 149 and 150: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 151 and 152: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 153 and 154: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 155 and 156: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 157 and 158: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 159 and 160: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 161 and 162: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 163 and 164: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 165 and 166: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 167 and 168: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 169 and 170: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 171 and 172: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 173 and 174: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 175 and 176: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 177 and 178: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 179 and 180: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 181 and 182: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 183 and 184: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 185 and 186: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 187 and 188: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 189: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 193 and 194: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 195 and 196: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 197 and 198: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 199 and 200: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 201 and 202: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 203 and 204: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 205 and 206: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 207 and 208: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 209 and 210: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 211 and 212: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 213 and 214: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 215 and 216: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 217 and 218: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 219 and 220: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 221 and 222: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 223 and 224: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 225 and 226: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 227 and 228: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
- Page 229 and 230: Deutsche Bank 01 - Management Repor
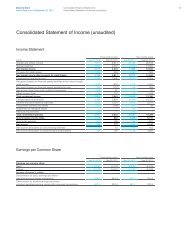
- Page 231 and 232: Consolidated Financial Statements C
- Page 233 and 234: Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 235 and 236: Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 237 and 238: Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 239 and 240: Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 241 and 242:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 243 and 244:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 245 and 246:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 247 and 248:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 249 and 250:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 251 and 252:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 253 and 254:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 255 and 256:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 257 and 258:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 259 and 260:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 261 and 262:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 263 and 264:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 265 and 266:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 267 and 268:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 269 and 270:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 271 and 272:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 273 and 274:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 275 and 276:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 277 and 278:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 279 and 280:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 281 and 282:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 283 and 284:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 285 and 286:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 287 and 288:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 289 and 290:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 291 and 292:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 293 and 294:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 295 and 296:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 297 and 298:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 299 and 300:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 301 and 302:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 303 and 304:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 305 and 306:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 307 and 308:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 309 and 310:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 311 and 312:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 313 and 314:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 315 and 316:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 317 and 318:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 319 and 320:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 321 and 322:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 323 and 324:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 325 and 326:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 327 and 328:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 329 and 330:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 331 and 332:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 333 and 334:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 335 and 336:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 337 and 338:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 339 and 340:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 341 and 342:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 343 and 344:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 345 and 346:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 347 and 348:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 349 and 350:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 351 and 352:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 353 and 354:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 355 and 356:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 357 and 358:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 359 and 360:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 361 and 362:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 363 and 364:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 365 and 366:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 367 and 368:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 369 and 370:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 371 and 372:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 373 and 374:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 375 and 376:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 377 and 378:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 379 and 380:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 381 and 382:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 383 and 384:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 385 and 386:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 387 and 388:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 389 and 390:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 391 and 392:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 393 and 394:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 395 and 396:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 397 and 398:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 399 and 400:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 401 and 402:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 403 and 404:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 405 and 406:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 407 and 408:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 409 and 410:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 411 and 412:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 413 and 414:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 415 and 416:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 417 and 418:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 419 and 420:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 421 and 422:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 423 and 424:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 425 and 426:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 427 and 428:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 429 and 430:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 431 and 432:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 433 and 434:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 435 and 436:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 437 and 438:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 439 and 440:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 441 and 442:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 443 and 444:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 445 and 446:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 447 and 448:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 449 and 450:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 451 and 452:
Deutsche Bank 02 - Consolidated Fin
- Page 453 and 454:
Confirmations Independent Auditors
- Page 455 and 456:
Deutsche Bank 03 - Confirmations 37
- Page 457 and 458:
Corporate Governance Statement / Co
- Page 459 and 460:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 461 and 462:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 463 and 464:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 465 and 466:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 467 and 468:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 469 and 470:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 471 and 472:
Deutsche Bank 04 - Corporate Govern
- Page 473 and 474:
Supplementary Information Managemen
- Page 475 and 476:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 477 and 478:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 479 and 480:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 481 and 482:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 483 and 484:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 485 and 486:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 487 and 488:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 489 and 490:
Deutsche Bank 05 - Supplementary In
- Page 492:
2011 April 28, 2011 Interim Report