Download the supplement (208 p.) - KCE
Download the supplement (208 p.) - KCE
Download the supplement (208 p.) - KCE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
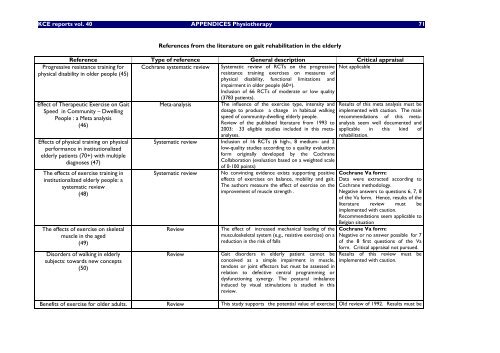
<strong>KCE</strong> reports vol. 40 APPENDICES Physio<strong>the</strong>rapy 71<br />
References from <strong>the</strong> literature on gait rehabilitation in <strong>the</strong> elderly<br />
Reference Type of reference General description Critical appraisal<br />
Progressive resistance training for Cochrane systematic review Systematic review of RCTs on <strong>the</strong> progressive Not applicable<br />
physical disability in older people (45)<br />
resistance training exercises on measures of<br />
physical disability, functional limitations and<br />
Effect of Therapeutic Exercise on Gait<br />
Meta-analysis<br />
impairment in older people (60+).<br />
Inclusion of 66 RCTs of moderate or low quality<br />
(3783 patients).<br />
The influence of <strong>the</strong> exercise type, intensity and Results of this meta analysis must be<br />
Speed in Community Dwelling<br />
dosage to produce a change in habitual walking implemented with caution. The main<br />
People : a Meta analysis<br />
(46)<br />
speed of community-dwelling elderly people.<br />
Review of <strong>the</strong> published literature from 1993 to<br />
2003: 33 eligible studies included in this meta-<br />
recommendations of this metaanalysis<br />
seem well documented and<br />
applicable in this kind of<br />
analyses.<br />
rehabilitation.<br />
Effects of physical training on physical Systematic review Inclusion of 16 RCTs (6 high-, 8 medium- and 2<br />
performance in institutionalized<br />
low-quality studies according to a quality evaluation<br />
elderly patients (70+) with multiple<br />
diagnoses (47)<br />
form originally developed by <strong>the</strong> Cochrane<br />
Collaboration (evaluation based on a weighted scale<br />
of 0-100 points)<br />
The effects of exercise training in<br />
Systematic review No convincing evidence exists supporting positive Cochrane Va form:<br />
institutionalized elderly people: a<br />
effects of exercises on balance, mobility and gait. Data were extracted according to<br />
systematic review<br />
(48)<br />
The authors measure <strong>the</strong> effect of exercise on <strong>the</strong> Cochrane methodology.<br />
improvement of muscle strength .<br />
Negative answers to questions 6, 7, 8<br />
of <strong>the</strong> Va form. Hence, results of <strong>the</strong><br />
literature review must be<br />
The effects of exercise on skeletal<br />
Review<br />
implemented with caution.<br />
Recommendations seem applicable to<br />
Belgian situation<br />
The effect of increased mechanical loading of <strong>the</strong> Cochrane Va form:<br />
muscle in <strong>the</strong> aged<br />
(49)<br />
musculoskeletal system (e.g., resistive exercise) on a<br />
reduction in <strong>the</strong> risk of falls<br />
Negative or no answer possible for 7<br />
of <strong>the</strong> 8 first questions of <strong>the</strong> Va<br />
form. Critical appraisal not pursued.<br />
Disorders of walking in elderly<br />
Review Gait disorders in elderly patient cannot be Results of this review must be<br />
subjects: towards new concepts<br />
conceived as a simple impairment in muscle, implemented with caution.<br />
(50)<br />
tendons or joint effectors but must be assessed in<br />
relation to defective central programming or<br />
dysfunctioning synergy. The postural imbalance<br />
induced by visual stimulations is studied in this<br />
review.<br />
Benefits of exercise for older adults. Review This study supports <strong>the</strong> potential value of exercise Old review of 1992. Results must be