View PDF Version - RePub - Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam
View PDF Version - RePub - Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam
View PDF Version - RePub - Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
probably caused by the less efficient release of this chromosome during cell lysis.<br />
genomic; E<br />
eDNA:<br />
probe A<br />
t(4;22)<br />
E<br />
=<br />
probe B<br />
5' MN1 axon ,SS\,S\SS'''SS\\\\\''SSSSSSSSSSS'J<br />
probe C<br />
Telomere<br />
+---<br />
Centromere<br />
kb<br />
21<br />
5,1 -<br />
4.3 -<br />
probe A probe n prohe C<br />
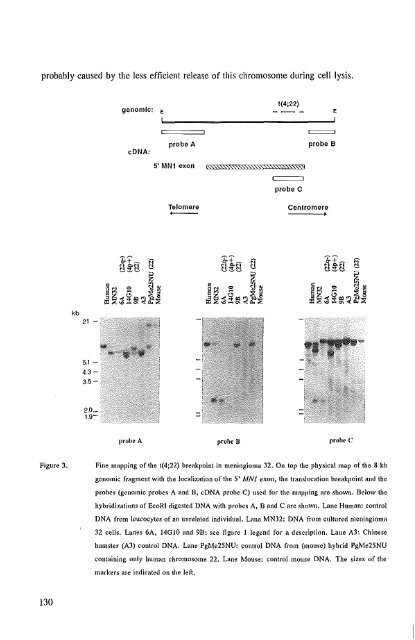
Figure 3,<br />
Fine mapping of the 1(4;22) breakpoint in meningioma 32. On top the physical map of the 8 kb<br />
genomic fragment with the localization of the 5' MNJ exon, the translocation breakpoint and the<br />
probes (genomic probes A and H, eDNA probe C) used for the mapping are shown. Below {he<br />
hybridizations of EcoRI digested DNA with probes A, Band C are shown. Lane Human: control<br />
DNA from leucocytes of an unrelated individual. Lane MN32: DNA (rom cultured nleningioma<br />
32 cells. Lanes 6A, 14G1O and 9B, see figure 1 legend for a description. Lane A3: Chinese<br />
hamster (A3) control DNA, Lane PgMe25NU: control DNA from (mouse) hybrid PgMe25NU<br />
containing only human chromosome 22, Lane Mouse: control mouse DNA, The sizes of the<br />
markers are indicated on the left,<br />
130