- Page 1:
GENES ON CHROMOSOME 22 INVOLVED IN
- Page 4 and 5:
PROMOTmCOMMIssm Promotor: Prof. Dr.
- Page 6 and 7:
Contents List of abbreviations 9 Ch
- Page 9:
List of abbreviations APC bp DCC FA
- Page 13 and 14:
1 Cancer is a genetic disease It is
- Page 15 and 16:
transformation came from somatic ce
- Page 17 and 18:
to tumorigenesis if a mutation inac
- Page 19 and 20:
is that this interaction inactivate
- Page 21 and 22:
endogenous wt p53 by forming mixed
- Page 23 and 24:
Recent studies in these families ha
- Page 25 and 26:
In about 15% of all colon tumors an
- Page 27 and 28:
e explained by assuming that the nu
- Page 29 and 30:
3.6 The NFl gene Neurofibromatosis
- Page 31 and 32:
4 MENINGIOMA 4.1 Cells of origin In
- Page 33 and 34:
fossa and foramen magnum), convexit
- Page 35 and 36:
early cell cultures the presence of
- Page 37 and 38:
gene (Dumanski et aI., NNFF consort
- Page 39 and 40:
et aI., 1991b; Larsson et aI., 1990
- Page 41 and 42:
6 References Aaltonen LA, Peltomiik
- Page 43 and 44:
(1988) SV40 large tumor antigen for
- Page 45 and 46:
Haber DA, Buckler AJ, Glaser T, Cal
- Page 47 and 48:
carcinomas. Genes Chrom Cancer 2:19
- Page 49 and 50:
Pelletier J, Breunin~ W, Kashtan CE
- Page 51 and 52:
Stratton MR, Darling J, Lantos PL,
- Page 53:
Chapter II Isolatioll alld characte
- Page 56 and 57:
SHORT COMMUNICATION TABLE 1 Charact
- Page 59:
Appendix A lIew polymorphic probe 0
- Page 62 and 63:
Nudeic Acids Research, Vol. 19, No.
- Page 65:
Chapter III Cytogenetic, molecular
- Page 68 and 69:
Introduction Meningiomas are consid
- Page 70 and 71:
defined by evaluating 6 histologica
- Page 72 and 73:
number of clonal chromosomal abnorm
- Page 74 and 75:
#22 status No. Sex/Age (yr) Site of
- Page 76 and 77:
#22 slattls No. SexiAge (yr) Site o
- Page 78 and 79:
#22 status No. Sex/Age (yr) Site of
- Page 80 and 81:
Table 2. Comparison of FISH, cytoge
- Page 82 and 83: No. Days in Karyotypes andlor clona
- Page 84 and 85: No. Days in Karyotypes and/or clona
- Page 86 and 87: to map both breakpoints (data not s
- Page 88 and 89: Statistical analyses concerning age
- Page 90 and 91: Tuble 4. Frequency tables between d
- Page 92 and 93: from adult patients, indicating tha
- Page 94 and 95: Acknowledgements This study was sup
- Page 96 and 97: McDermid HE, Duncan AMV, Higgins MJ
- Page 99 and 100: Chapter IV Familial anaplastic epen
- Page 101 and 102: Familial anaplastic ependymoma: evi
- Page 103 and 104: PATIENT A, born 1977, presented at
- Page 105 and 106: Microscopic examination (patients A
- Page 107 and 108: (Lekanne Deprez et aI., 1994). Tabl
- Page 109 and 110: Chapter V A t(4;22) ill a meningiom
- Page 111 and 112: Am. J. HI/m. Genet. 48:783-790, 199
- Page 113 and 114: Putative Tumor-suppressor Gene in M
- Page 115 and 116: Putative Tumor-suppressor Gene in M
- Page 117 and 118: Putative Tumor-suppressor Gene in M
- Page 119 and 120: Chapter VI Molecular clolling of a
- Page 121 and 122: Molecular Cloning of a Gene Disrupt
- Page 123 and 124: to playa role in the development of
- Page 125 and 126: total sheared human genomic DNA bef
- Page 127 and 128: Genomic cosmid contig spanning the
- Page 129 and 130: probe A is conserved in hamster DNA
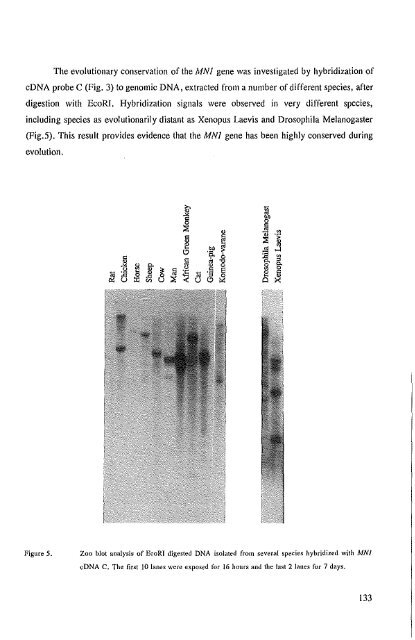
- Page 131: Southerll, 1l0l1hern blots and evol
- Page 135 and 136: A " l ... aGAP~RAGC EPOV~SR~AGQGE ;
- Page 137 and 138: postulates that the first AUG codon
- Page 139 and 140: Bijlsma EK, Brouwer~Mladin R, Bosch
- Page 141 and 142: Tanaka N, Nishisho I, Yamamoto 1'.1
- Page 143 and 144: Chapter VII Constitutional DNA-leve
- Page 145 and 146: GENES, CHROMOSOMES & CANCER 9;124-1
- Page 147 and 148: LfKANNf DfPREZ fT AL TABLE I. Cytog
- Page 149 and 150: LEKANNE DEPRF2 ET AL could be that
- Page 151 and 152: Chapter VIII Frequent NF2 gene tran
- Page 153 and 154: Am.'. HIIIII. Gellet. 54:1022-1029,
- Page 155 and 156: Lekanne Deprez ct al. Table I Oligo
- Page 157 and 158: Table 2 Nfl Gene-Transcript Mutatio
- Page 159 and 160: Lebnne Deprez et lli. observed at a
- Page 161 and 162: Summary and Discussion Meningioma i
- Page 163 and 164: translocation (Chapter V). These hy
- Page 165 and 166: were derived from patients with mor
- Page 167 and 168: Samenvatting Meningeomen zUn goedaa
- Page 169 and 170: het gebied rondom het MNI gen te be
- Page 171 and 172: Curriculum vitae 30 juni 1965 gebor
- Page 173 and 174: List of publications I) van 't Veer
- Page 175 and 176: Nawoord Dit boekje is 101 sland gek