The System Manual of SOL-20 - History of Computers
The System Manual of SOL-20 - History of Computers
The System Manual of SOL-20 - History of Computers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION<br />
Sol THEORY OF OPERATION<br />
SECTION VIII<br />
In the Sol-<strong>20</strong>, the S-100 Bus structure takes the form <strong>of</strong> a<br />
five-slot backplane board. It consists <strong>of</strong> a printed circuit board<br />
with 100 lines (50 on each side) and five edge connectors on which<br />
like-numbered pins are connected from one connector to another.<br />
Functionally, the Sol version <strong>of</strong> the S-100 Bus is comprised <strong>of</strong>:<br />
1. Sixteen output address lines from the CPU which are input<br />
to all external memory and I/O circuitry. (Direct memory<br />
access (DMA) devices must generate addresses on these<br />
lines for DMA transfers.)<br />
2. Eight data input/output lines that transfer data between<br />
external memory and I/O devices and the CPU or DMA devices.<br />
(<strong>The</strong>se eight lines are paralleled with eight<br />
other bus lines.)<br />
3. Eight status output lines from the CPU support logic:<br />
Memory and I/O devices use status signals to obtain information<br />
concerning the nature <strong>of</strong> the CPU cycle. (DMA<br />
devices must generate these signals for DMA transfers.)<br />
4. Nine processor command and control lines: Six <strong>of</strong> these<br />
are output signals from the CPU support logic; three <strong>of</strong><br />
them are input signals to the CPU support logic from<br />
memory and I/O devices. (In a DMA transfer, the DMA device<br />
assumes control <strong>of</strong> these lines.)<br />
5. Five disable lines: Four <strong>of</strong> these are supplied by a DMA<br />
device to disable the tri-state drivers on the CPU outputs<br />
during DMA transfers. <strong>The</strong> fifth is a derivative <strong>of</strong><br />
the DBIN output from the CPU, and it is used to disable<br />
any memory addressed in Page ft. Use <strong>of</strong> this disable is<br />
optional with a jumper.<br />
6. Two input lines to the CPU support logic which are used<br />
for requesting a wait period. One is used by memory and<br />
I/O devices and the other by external devices.<br />
7. Six power supply lines which supply power to expansion<br />
modules.<br />
8. Three clock lines.<br />
9. Four special purpose signal lines.<br />
10. Thirty-one unused lines.<br />
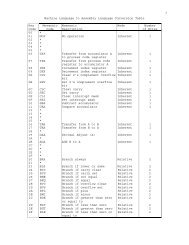
Definitions for each S-100 Bus line, as used in the Sol, are<br />
provided on Pages AVII-3 through AVII-6 in Appendix VII.<br />
In addition to the S-100 Bus structure, Sol also uses an<br />
eight-line keyboard input port, an eight-line parallel input port,<br />
VIII-2