Direct Power and Torque Control of AC/DC/AC Converter-Fed ...
Direct Power and Torque Control of AC/DC/AC Converter-Fed ...
Direct Power and Torque Control of AC/DC/AC Converter-Fed ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
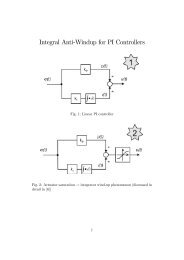
4. <strong>Direct</strong> <strong>Power</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Torque</strong> <strong>Control</strong> with Space Vector Modulation – DPTC-SVM<br />
mS<br />
Pe<br />
= pb<br />
ΩmΨ<br />
SxISy<br />
(4. 6)<br />
2<br />
Moreover, it can be assumed (neglecting power losses) that electromagnetic power <strong>of</strong><br />
the IM is equal to an active power delivered to the motor<br />
P<br />
p<br />
m<br />
2<br />
Ω Ψ<br />
I<br />
P = P<br />
e<br />
VSI<br />
, hence:<br />
S<br />
VSI<br />
=<br />
b m Sx Sy<br />
(4. 7)<br />
But this is not sufficient assumption because <strong>of</strong> power losses P losses<br />
in the real<br />
system, so it should be written:<br />
m<br />
2<br />
S<br />
P<br />
VSI<br />
= pb<br />
ΩmΨ<br />
SxI<br />
Sy<br />
+<br />
P<br />
losses<br />
Further, please consider a situation at st<strong>and</strong> still ( = 0)<br />
m<br />
(4. 8)<br />
Ω when nominal torque is<br />
applied. In such a case the electromagnetic power will be zero but the IM power P<br />
VSI<br />
will have a significant value. Estimation <strong>of</strong> this power is quite difficult, because the<br />
parameters <strong>of</strong> the IM <strong>and</strong> power switches are needed. Hence, for simplicity <strong>of</strong> the<br />
control structure a power estimator based on comm<strong>and</strong> stator voltage<br />
current I<br />
S<br />
will be taken into consideration:<br />
U<br />
Sc<br />
<strong>and</strong> actual<br />
VSI<br />
( I U I U )<br />
3<br />
P = + 2<br />
Sx<br />
Sxc<br />
Sy<br />
Syc<br />
(4. 9)<br />
4.2.1. Analysis <strong>of</strong> the <strong>Power</strong> Response Time Constant<br />
Based on Eq. (3.68) the time constant delay <strong>of</strong> the VSR response T IT<br />
is<br />
determined. With assumption that power losses <strong>of</strong> the converters can be neglected,<br />
power tracking performance can be expressed by:<br />
VSR<br />
() PVSRc<br />
+ sTIT<br />
P<br />
1<br />
s = (4. 10)<br />
1<br />
Similarly for the VSI can be written:<br />
VSI<br />
() PVSIc<br />
+ sTIF<br />
P<br />
1<br />
s = (4. 11)<br />
1<br />
Where, T<br />
IF<br />
is the equivalent time constant <strong>of</strong> the VSI step response.<br />
4.2.2. Energy <strong>of</strong> the <strong>DC</strong>-link Capacitor<br />
The <strong>DC</strong>-link voltage can be described as (for more detail see Section 2.5.2):<br />
71















![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)