- Page 1 and 2:
New Zealand Autism Spectrum Disorde
- Page 3 and 4:
New Zealand Autism Spectrum Disorde
- Page 5 and 6:
Whakapüpütia mai ö mänuka kia k
- Page 7 and 8:
“I am tired of having to do 100%
- Page 9 and 10:
2.3 Physical well-being............
- Page 11 and 12:
References.........................
- Page 13 and 14:
Overview “It is common for me and
- Page 15 and 16:
Overview Overview Purpose of the Ne
- Page 17 and 18:
Overview Overview Preface I was bor
- Page 19 and 20:
Overview Overview educational princ
- Page 21 and 22:
Overview Overview Consultation To f
- Page 23 and 24:
Overview Overview Executive summary
- Page 25 and 26:
Overview Overview Key recommendatio
- Page 27 and 28:
Overview Overview Key recommendatio
- Page 29 and 30:
Overview Overview Key recommendatio
- Page 31 and 32:
Overview Overview Key recommendatio
- Page 33 and 34:
Overview Overview Key recommendatio
- Page 35 and 36:
Overview Overview Part 7 Mäori per
- Page 37 and 38:
Overview Overview or to changes in
- Page 39 and 40:
Part 1 Diagnosis and initial assess
- Page 41 and 42:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 43 and 44:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 45 and 46:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 47 and 48:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 49 and 50:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 51 and 52:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 53 and 54:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 55 and 56:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 57 and 58:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 59 and 60:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 61 and 62:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 63 and 64:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 65 and 66:
Part 1: Diagnosis and initial asses
- Page 67 and 68:
Part 2 Support for individuals, fam
- Page 69 and 70:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 71 and 72:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 73 and 74:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 75 and 76:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 77 and 78:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 79 and 80:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 81 and 82:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 83 and 84:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 85 and 86:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 87 and 88:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 89 and 90:
Part 2: Support for individuals, fa
- Page 91 and 92:
Part 3 Education for learners with
- Page 93 and 94:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 95 and 96:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 97 and 98:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 99 and 100:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 101 and 102:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 103 and 104:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 105 and 106:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 107 and 108:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 109 and 110:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 111 and 112:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 113 and 114:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 115 and 116:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 117 and 118:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 119 and 120:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 121 and 122:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 123 and 124:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 125 and 126:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 127 and 128:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 129 and 130:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 131 and 132:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 133 and 134:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 135 and 136:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 137 and 138:
Part 3: Education for learners with
- Page 139 and 140:
Part 4 Treatment and management of
- Page 141 and 142:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 143 and 144:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 145 and 146:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 147 and 148:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 149 and 150:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 151 and 152:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 153 and 154:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 155 and 156:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 157 and 158:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 159 and 160:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 161 and 162:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 163 and 164:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 165 and 166:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 167 and 168:
Part 4: Treatment and management of
- Page 169 and 170:
Part 5 Living in the community “I
- Page 171 and 172:
Part 5: Living in the community 5.1
- Page 173 and 174:
Part 5: Living in the community •
- Page 175 and 176:
Part 5: Living in the community pos
- Page 177 and 178:
Part 5: Living in the community •
- Page 179 and 180:
Part 5: Living in the community 5.2
- Page 181 and 182:
Part 5: Living in the community •
- Page 183 and 184:
Part 5: Living in the community all
- Page 185 and 186:
Part 5: Living in the community 5.3
- Page 187 and 188:
Part 5: Living in the community Vul
- Page 189 and 190:
Part 5: Living in the community Pol
- Page 191 and 192:
Part 6 Professional learning and de
- Page 193 and 194:
Part 6: Professional learning and d
- Page 195 and 196:
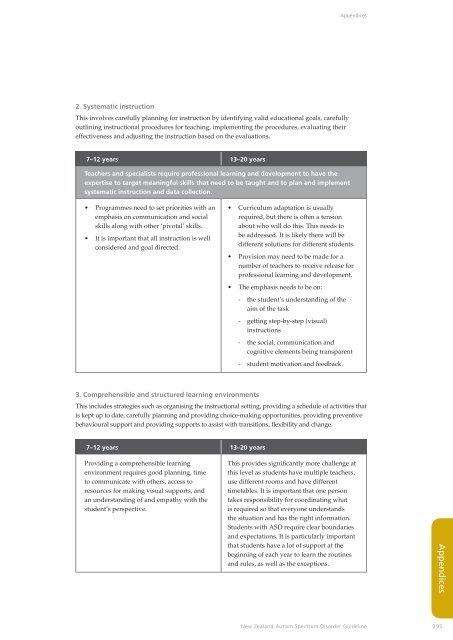
Part 6: Professional learning and d
- Page 197 and 198:
Part 6: Professional learning and d
- Page 199 and 200:
Part 6: Professional learning and d
- Page 201 and 202:
Part 6: Professional learning and d
- Page 203 and 204:
Part 7 Mäori perspectives “You c
- Page 205 and 206:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives This pa
- Page 207 and 208:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives Results
- Page 209 and 210:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives 7.2 Nat
- Page 211 and 212:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives Fewer r
- Page 213 and 214:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives ASD and
- Page 215 and 216:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives be assu
- Page 217 and 218:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives It was
- Page 219 and 220:
Part 7: Mäori perspectives care se
- Page 221 and 222:
Part 8 Pacific peoples’ perspecti
- Page 223 and 224:
Part 8: Pacific peoples’ perspect
- Page 225 and 226:
Part 8: Pacific peoples’ perspect
- Page 227 and 228:
References “It is not wrong to th
- Page 229 and 230:
References 29. English A, Essex J.
- Page 231 and 232:
References 74. Krug DA, Arick JR. K
- Page 233 and 234:
References 128. McCabe P, McCabe E,
- Page 235 and 236:
References 180. Dunlap G, Fox L. Su
- Page 237 and 238:
References 223. Charlop-Christy MH,
- Page 239 and 240:
References 274. Green CJ, Bassett K
- Page 241 and 242:
References 320. Paavonen J, Niemine
- Page 243 and 244:
References 368. Unger DD, Parent W,
- Page 245 and 246:
References 417. Ministry of Health.
- Page 247 and 248:
Glossary “It’s like attacking a
- Page 249 and 250: Glossary Asperger syndrome (AS) Ass
- Page 251 and 252: Glossary Cognitive assessment Cogni
- Page 253 and 254: Glossary Discrete trial training (D
- Page 255 and 256: Glossary Facilitated communication
- Page 257 and 258: Glossary Inclusion Inclusive settin
- Page 259 and 260: Glossary Narrative assessment Natur
- Page 261 and 262: Glossary Phenotype Physiotherapy Pi
- Page 263 and 264: Glossary Regional Intellectual Disa
- Page 265 and 266: Glossary Social decision-making str
- Page 267 and 268: Glossary Tuberose sclerosis Typical
- Page 269 and 270: Glossary Tamariki Ora Tapu Te reo M
- Page 271 and 272: Appendices “I am tired of having
- Page 273 and 274: Appendices Consultation The detaile
- Page 275 and 276: Appendices Practice questions and t
- Page 277 and 278: Appendices Where a recommendation i
- Page 279 and 280: Appendices Sue Robertson (leader of
- Page 281 and 282: Appendices Mary Smith Verifier Mini
- Page 283 and 284: Appendices 3. Steering Group Basia
- Page 285 and 286: Appendices 4. Senior Officials Grou
- Page 287 and 288: Appendices Name Position Additional
- Page 289 and 290: Appendices Name Position Additional
- Page 291 and 292: Appendices 2. Expert peer review Th
- Page 293 and 294: Appendices 299.80 Asperger’s Diso
- Page 295 and 296: Appendices Appendix 5:The role of d
- Page 297 and 298: Appendices 2. What population has t
- Page 299: Appendices Recommendation: Formal b
- Page 303 and 304: Appendices 5. Functional approach t
- Page 305 and 306: Appendices Play is used as primary
- Page 307 and 308: New Zealand Autism Spectrum Disorde
- Page 309 and 310: Generic name Trade name NZ prescrib
- Page 311: Generic name Trade name NZ prescrib