The Palestinian Economy. Theoretical and Practical Challenges
The Palestinian Economy. Theoretical and Practical Challenges
The Palestinian Economy. Theoretical and Practical Challenges
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
404<br />
Makhool<br />
marital status, <strong>and</strong> industry group.) <strong>and</strong> the dependent variable (labour force status)<br />
(See Table 3).<br />
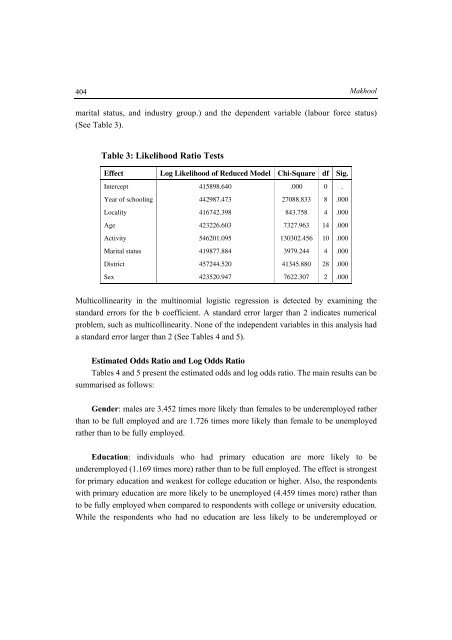
Table 3: Likelihood Ratio Tests<br />
Effect Log Likelihood of Reduced Model Chi-Square df Sig.<br />
Intercept 415898.640 .000 0 .<br />
Year of schooling 442987.473 27088.833 8 .000<br />
Locality 416742.398 843.758 4 .000<br />
Age 423226.603 7327.963 14 .000<br />
Activity 546201.095 130302.456 10 .000<br />
Marital status 419877.884 3979.244 4 .000<br />
District 457244.520 41345.880 28 .000<br />
Sex 423520.947 7622.307 2 .000<br />
Multicollinearity in the multinomial logistic regression is detected by examining the<br />
st<strong>and</strong>ard errors for the b coefficient. A st<strong>and</strong>ard error larger than 2 indicates numerical<br />
problem, such as multicollinearity. None of the independent variables in this analysis had<br />
a st<strong>and</strong>ard error larger than 2 (See Tables 4 <strong>and</strong> 5).<br />
Estimated Odds Ratio <strong>and</strong> Log Odds Ratio<br />
Tables 4 <strong>and</strong> 5 present the estimated odds <strong>and</strong> log odds ratio. <strong>The</strong> main results can be<br />
summarised as follows:<br />
Gender: males are 3.452 times more likely than females to be underemployed rather<br />
than to be full employed <strong>and</strong> are 1.726 times more likely than female to be unemployed<br />
rather than to be fully employed.<br />
Education: individuals who had primary education are more likely to be<br />
underemployed (1.169 times more) rather than to be full employed. <strong>The</strong> effect is strongest<br />
for primary education <strong>and</strong> weakest for college education or higher. Also, the respondents<br />
with primary education are more likely to be unemployed (4.459 times more) rather than<br />
to be fully employed when compared to respondents with college or university education.<br />
While the respondents who had no education are less likely to be underemployed or