- Page 2 and 3:
Molecular Medical Parasitology
- Page 4 and 5:
Molecular Medical Parasitology Edit
- Page 6 and 7:
Contents List of contributors Prefa
- Page 8 and 9:
List of contributors Mark Blaxter,
- Page 10 and 11:
LIST OF CONTRIBUTORS ix Richard. J.
- Page 12 and 13:
Preface Parasitology was born as th
- Page 14 and 15:
S E C T I O N I MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
- Page 16 and 17:
C H A P T E R 1 Parasite genomics M
- Page 18 and 19:
TABLE 1.1 Parasite genomes: genome
- Page 20 and 21:
GENERATING GENOMICS DATA 7 differen
- Page 22 and 23: GENERATING GENOMICS DATA 9 TABLE 1.
- Page 24 and 25: GENERATING GENOMICS DATA 11 called
- Page 26 and 27: GENERATING GENOMICS DATA 13 200 000
- Page 28 and 29: BIOINFORMATICS AND THE ANALYSIS OF
- Page 30 and 31: THE POST-GENOMICS ERA, AND THE OTHE
- Page 32 and 33: THE PARASITES AND THEIR GENOMES 19
- Page 34 and 35: THE PARASITES AND THEIR GENOMES 21
- Page 36 and 37: THE PARASITES AND THEIR GENOMES 23
- Page 38 and 39: THE PARASITES AND THEIR GENOMES 25
- Page 40 and 41: FURTHER READING 27 treated with a d
- Page 42 and 43: C H A P T E R 2 RNA processing in p
- Page 44 and 45: TRANS-SPLICING 31 cis trans Exon 1
- Page 46 and 47: TRANS-SPLICING 33 snRNPs (small nuc
- Page 48 and 49: TRANS-SPLICING 35 trans cis U2AF35
- Page 50 and 51: RNA EDITING 37 P AAAA... AAAA... AA
- Page 52 and 53: RNA EDITING 39 entire transcript re
- Page 54 and 55: RNA EDITING 41 5 Editing block C Ed
- Page 56 and 57: RNA EDITING 43 microscopy) approach
- Page 58 and 59: FURTHER READING 45 Nilsen, T.W. (19
- Page 60 and 61: C H A P T E R 3 Transcription Arthu
- Page 62 and 63: UNUSUAL MODES OF TRANSCRIPTION IN T
- Page 64 and 65: CLASS I TRANSCRIPTION IN TRYPANOSOM
- Page 66 and 67: CLASS I TRANSCRIPTION IN TRYPANOSOM
- Page 68 and 69: CLASS I TRANSCRIPTION IN TRYPANOSOM
- Page 70 and 71: CLASS II TRANSCRIPTION OF PROTEIN C
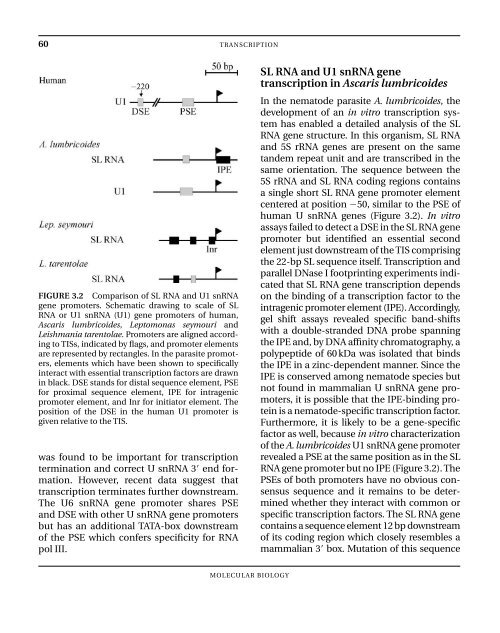
- Page 74 and 75: SL RNA AND U snRNA GENE TRANSCRIPTI
- Page 76 and 77: SL RNA AND U snRNA GENE TRANSCRIPTI
- Page 78 and 79: FURTHER READING 65 and switching in
- Page 80 and 81: C H A P T E R 4 Post-transcriptiona
- Page 82 and 83: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 84 and 85: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 86 and 87: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 88 and 89: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 90 and 91: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 92 and 93: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 94 and 95: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 96 and 97: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 98 and 99: POST-TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION IN
- Page 100 and 101: FURTHER READING 87 inhibition, it m
- Page 102 and 103: C H A P T E R 5 Antigenic variation
- Page 104 and 105: ANTIGENIC VARIATION AT THE STRUCTUR
- Page 106 and 107: ANTIGENIC VARIATION AT THE STRUCTUR
- Page 108 and 109: VSG Signal sequence Amino-terminal
- Page 110 and 111: GENETICS OF ANTIGENIC VARIATION 97
- Page 112 and 113: GENETICS OF ANTIGENIC VARIATION 99
- Page 114 and 115: GENETICS OF ANTIGENIC VARIATION 101
- Page 116 and 117: IMMUNE RESPONSES TO TRYPANOSOME INF
- Page 118 and 119: INNATE RESISTANCE, HUMAN SUSCEPTIBI
- Page 120 and 121: ANTIGENIC VARIATION IN MALARIA 107
- Page 122 and 123:
FURTHER READING 109 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
- Page 124 and 125:
C H A P T E R 6 Genetic and genomic
- Page 126 and 127:
‘FORWARD’ VS. ‘REVERSE’ GEN
- Page 128 and 129:
EXAMPLES OF ‘FORWARD’ GENETIC A
- Page 130 and 131:
EXAMPLES OF ‘FORWARD’ GENETIC A
- Page 132 and 133:
REVERSE GENETICS AND LEISHMANIA VIR
- Page 134 and 135:
VALIDATION OF CANDIDATE VIRULENCE G
- Page 136 and 137:
S E C T I O N II BIOCHEMISTRY AND C
- Page 138 and 139:
C H A P T E R 7 Energy metabolism P
- Page 140 and 141:
SUBCELLULAR ORGANIZATION OF AMITOCH
- Page 142 and 143:
CELL MEMBRANE Fructose [b] Glucose
- Page 144 and 145:
STEPS OF AMITOCHONDRIATE CORE METAB
- Page 146 and 147:
ENZYMATIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN AMITO
- Page 148 and 149:
ACTION OF NITROIMIDAZOLE DRUGS 135
- Page 150 and 151:
ENVOI 137 unambiguously reflect the
- Page 152 and 153:
FURTHER READING 139 Saavedra-Lira,
- Page 154 and 155:
THE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-PARNAS (EMP) PA
- Page 156 and 157:
THE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-PARNAS (EMP) PA
- Page 158 and 159:
THE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-PARNAS (EMP) PA
- Page 160 and 161:
THE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-PARNAS (EMP) PA
- Page 162 and 163:
THE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-PARNAS (EMP) PA
- Page 164 and 165:
WHY DO TRYPANOSOMATIDAE HAVE GLYCOS
- Page 166 and 167:
FURTHER READING 153 for use in agri
- Page 168:
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 155 as a hu
- Page 171 and 172:
158 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 173 and 174:
160 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 175 and 176:
162 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 177 and 178:
164 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 179 and 180:
166 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 181 and 182:
168 ENERGY METABOLISM - APICOMPLEXA
- Page 183 and 184:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 185 and 186:
172 PROTEIN METABOLISM PROTEINS (1)
- Page 187 and 188:
174 PROTEIN METABOLISM the C-termin
- Page 189 and 190:
176 PROTEIN METABOLISM and also, to
- Page 191 and 192:
178 PROTEIN METABOLISM values rangi
- Page 193 and 194:
180 PROTEIN METABOLISM of the plasm
- Page 195 and 196:
182 PROTEIN METABOLISM in vivo, in
- Page 197 and 198:
184 PROTEIN METABOLISM PROLINE Poly
- Page 199 and 200:
186 PROTEIN METABOLISM CO 2 Dec-SAM
- Page 201 and 202:
188 PROTEIN METABOLISM a cMDH has b
- Page 203 and 204:
190 PROTEIN METABOLISM Urea ARGININ
- Page 205 and 206:
192 PROTEIN METABOLISM been describ
- Page 207 and 208:
194 PROTEIN METABOLISM absence of g
- Page 209 and 210:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 211 and 212:
198 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES enable
- Page 213 and 214:
200 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES provide
- Page 215 and 216:
202 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES activit
- Page 217 and 218:
204 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES physiol
- Page 219 and 220:
206 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES Amitoch
- Page 221 and 222:
208 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES their a
- Page 223 and 224:
210 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES FIGURE
- Page 225 and 226:
212 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES FIGURE
- Page 227 and 228:
214 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES protein
- Page 229 and 230:
216 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES FIGURE
- Page 231 and 232:
218 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES FIGURE
- Page 233 and 234:
220 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES in Plas
- Page 235 and 236:
222 PURINES AND PYRIMIDINES whereas
- Page 237 and 238:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 239 and 240:
226 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES AF
- Page 241 and 242:
228 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES In
- Page 243 and 244:
230 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES po
- Page 245 and 246:
232 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES LP
- Page 247 and 248:
234 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES re
- Page 249 and 250:
236 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES sc
- Page 251 and 252:
A. sAP COOH [T][T](S/T)(S/T)(S/T)SS
- Page 253 and 254:
240 TRYPANOSOMATID CARBOHYDRATES Cr
- Page 255 and 256:
242 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING protein
- Page 257 and 258:
244 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING FIGURE
- Page 259 and 260:
246 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING 212.5 2
- Page 261 and 262:
248 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING cycle.
- Page 263 and 264:
250 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING V-H -A
- Page 265 and 266:
252 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING domain)
- Page 267 and 268:
254 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING the kno
- Page 269 and 270:
256 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING from in
- Page 271 and 272:
258 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING FIGURE
- Page 273 and 274:
260 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING ESAG4 (
- Page 275 and 276:
262 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING and ind
- Page 277 and 278:
264 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING ATPase
- Page 279 and 280:
266 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING G11XG
- Page 281 and 282:
268 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING a diffe
- Page 283 and 284:
270 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING rapid l
- Page 285 and 286:
272 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING cells w
- Page 287 and 288:
274 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING PfPPJ i
- Page 289 and 290:
276 INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING is cont
- Page 291 and 292:
278 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 293 and 294:
280 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 295 and 296:
282 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 297 and 298:
284 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 299 and 300:
286 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 301 and 302:
288 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 303 and 304:
290 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 305 and 306:
292 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 307 and 308:
294 PLASTIDS, MITOCHONDRIA, AND HYD
- Page 309 and 310:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 311 and 312:
298 HELMINTH SURFACES Important exc
- Page 313 and 314:
300 HELMINTH SURFACES protease inhi
- Page 315 and 316:
302 HELMINTH SURFACES volume, there
- Page 317 and 318:
304 HELMINTH SURFACES projecting si
- Page 319 and 320:
306 HELMINTH SURFACES schistosome t
- Page 321 and 322:
308 HELMINTH SURFACES re-establish
- Page 323 and 324:
310 HELMINTH SURFACES hepatic cells
- Page 325 and 326:
312 HELMINTH SURFACES lungs. Larvae
- Page 327 and 328:
314 HELMINTH SURFACES cuticle, whic
- Page 329 and 330:
316 HELMINTH SURFACES cuticle in th
- Page 331 and 332:
318 HELMINTH SURFACES mec-8 or sym-
- Page 333 and 334:
320 HELMINTH SURFACES current, when
- Page 335 and 336:
322 HELMINTH SURFACES The cuticle-h
- Page 337 and 338:
324 HELMINTH SURFACES are typically
- Page 339 and 340:
326 HELMINTH SURFACES or carrier pr
- Page 341 and 342:
328 HELMINTH SURFACES of tyrosine-b
- Page 343 and 344:
330 HELMINTH SURFACES blood. The ge
- Page 345 and 346:
332 HELMINTH SURFACES Mutations in
- Page 347 and 348:
334 HELMINTH SURFACES in the hypode
- Page 349 and 350:
336 HELMINTH SURFACES (including H-
- Page 351 and 352:
338 HELMINTH SURFACES Blaxter, M.L.
- Page 353 and 354:
340 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 355 and 356:
342 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 357 and 358:
344 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 359 and 360:
346 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 361 and 362:
348 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 363 and 364:
350 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 365 and 366:
352 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 367 and 368:
354 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 369 and 370:
356 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 371 and 372:
358 ENERGY METABOLISM IN HELMINTHS
- Page 373 and 374:
360 NEUROTRANSMITTERS CO 2 H NH 2 G
- Page 375 and 376:
362 NEUROTRANSMITTERS TABLE 15.1 An
- Page 377 and 378:
364 NEUROTRANSMITTERS more arms tha
- Page 379 and 380:
366 NEUROTRANSMITTERS the surroundi
- Page 381 and 382:
368 NEUROTRANSMITTERS proteins requ
- Page 383 and 384:
370 NEUROTRANSMITTERS FIGURE 15.11
- Page 385 and 386:
372 NEUROTRANSMITTERS FIGURE 15.13
- Page 387 and 388:
374 NEUROTRANSMITTERS sensitivity t
- Page 389 and 390:
376 NEUROTRANSMITTERS TABLE 15.3 Cl
- Page 391 and 392:
378 NEUROTRANSMITTERS crossed the c
- Page 393 and 394:
380 NEUROTRANSMITTERS have been tes
- Page 395 and 396:
382 NEUROTRANSMITTERS C-terminals a
- Page 397 and 398:
384 NEUROTRANSMITTERS Davis and Str
- Page 399 and 400:
386 NEUROTRANSMITTERS Cephalic gang
- Page 401 and 402:
388 NEUROTRANSMITTERS myoexcitation
- Page 403 and 404:
390 NEUROTRANSMITTERS is phosphoryl
- Page 405 and 406:
392 NEUROTRANSMITTERS many other an
- Page 407 and 408:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 409 and 410:
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
- Page 411 and 412:
398 DRUG RESISTANCE of some of the
- Page 413 and 414:
400 DRUG RESISTANCE It is now estim
- Page 415 and 416:
402 DRUG RESISTANCE is again assume
- Page 417 and 418:
404 DRUG RESISTANCE An alternative
- Page 419 and 420:
406 DRUG RESISTANCE clinical eviden
- Page 421 and 422:
408 DRUG RESISTANCE FIGURE 16.4 Fol
- Page 423 and 424:
410 DRUG RESISTANCE Using similar s
- Page 425 and 426:
412 DRUG RESISTANCE whether these r
- Page 427 and 428:
414 DRUG RESISTANCE FIGURE 16.5 Str
- Page 429 and 430:
416 DRUG RESISTANCE FIGURE 16.6 Try
- Page 431 and 432:
418 DRUG RESISTANCE has permitted e
- Page 433 and 434:
420 DRUG RESISTANCE FIGURE 16.7 Dru
- Page 435 and 436:
422 DRUG RESISTANCE near future. Th
- Page 437 and 438:
424 DRUG RESISTANCE million new inf
- Page 439 and 440:
426 DRUG RESISTANCE some 50 million
- Page 441 and 442:
428 DRUG RESISTANCE pharynx, the bo
- Page 443 and 444:
430 DRUG RESISTANCE efforts for glo
- Page 445 and 446:
432 DRUG RESISTANCE and resistance
- Page 447 and 448:
434 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS TABLE 17.1
- Page 449 and 450:
436 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS TABLE 17.1
- Page 451 and 452:
438 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS transmissi
- Page 453 and 454:
440 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS H 2 C H H
- Page 455 and 456:
442 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS parasites
- Page 457 and 458:
444 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS neuropsych
- Page 459 and 460:
446 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS of toxic f
- Page 461 and 462:
448 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS Future con
- Page 463 and 464:
450 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS Melarsopro
- Page 465 and 466:
452 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS prevention
- Page 467 and 468:
454 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS resulting
- Page 469 and 470:
456 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS for S. ste
- Page 471 and 472:
458 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS are though
- Page 473 and 474:
460 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS FIGURE 17.
- Page 475 and 476:
462 MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS Marr, J.J.
- Page 477 and 478:
464 INDEX Aldolase, 143 Plasmodium
- Page 479 and 480:
466 INDEX Ascofuranone, 143 ASCUT-1
- Page 481 and 482:
468 INDEX Cnidarians, RNA trans-spl
- Page 483 and 484:
470 INDEX Entamoeba, 125 Ca 2 metab
- Page 485 and 486:
472 INDEX Glucose-6-phosphate dehyd
- Page 487 and 488:
474 INDEX Ivermectin, 398, 427, 455
- Page 489 and 490:
476 INDEX Maduramicin, 412 Major va
- Page 491 and 492:
478 INDEX Nitric oxide: neurotransm
- Page 493 and 494:
480 INDEX calcium-binding proteins,
- Page 495 and 496:
482 INDEX Pyrimidine transport, 200
- Page 497 and 498:
484 INDEX Succinate:rhodoquinone ox
- Page 499 and 500:
486 INDEX genome, 21 survey sequenc
- Page 501:
488 INDEX U small nuclear RNA (snRN