East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
103<br />
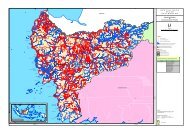
The greatest economic risks from inland flooding is concentrated in Samarinda and<br />
Balikpapan. The two cities contain half of the province’s population as well as much of the major<br />
businesses and factories; thus, they have more at stake simply by having more assets. Urban areas<br />
are also more vulnerable due to their higher population concentrations and fixed assets; these are<br />
exacerbated by poor drainage systems. Rural communities, especially those located on floodprone<br />
rivers, are more resilient to changing flood levels by building floating homes or houses on<br />
stilts that can be adjusted.<br />
Adaptive capacity of rural coastal plains is higher than urban areas<br />
Rural communities that historically lived close to<br />
the river developed techniques to adapt…<br />
▪ River communities have for centuries managed<br />
and adapted to changing flood levels by<br />
building floating homes or houses on adjustable<br />
stilts<br />
▪ Farming activities and transportation might be<br />
affected in the long term requiring populations<br />
to relocate<br />
Houses built on stilts along the Mahakam<br />
SOURCE: Mr Nathan, Munich Re, Kaltim Post, literature search<br />
DRAFT<br />
Adaptive measures to inland flooding require both upstream and downstream initiatives.<br />
Watersheds in the upstream areas of rivers play an important role in regulating rainfall in rivers.<br />
Preserving these watersheds from logging or conversion to agricultural land or plantations will<br />
mitigate any increase in inland flooding. A simple yet effective downstream measure is hiring staff<br />
to clean garbage out of the storm and sewer system to allow for better drainage. Like in coastal<br />
flooding, better disaster management including warnings and emergency shelter, is an important<br />
tool for both cities’ to adapt to inland flooding.<br />
PILOT PROJECTS<br />
… while urban areas with higher population<br />
concentrations and fixed assets struggle<br />
▪ Flooding in urban areas has historically been a<br />
key risk because of severe rains and a large<br />
low-gradient river system<br />
▪ Lack of drainage and poorly maintained and<br />
cleaned sewage systems result in slow<br />
drainage in urban areas<br />
Flooding after rains in Samarinda, March 2010<br />
Adaptation for coastal flooding in Balikpapan is a potential pilot project for <strong>East</strong><br />
<strong>Kalimantan</strong>. To implement the identified adaptation measures above, more in-depth analysis is<br />
needed on the cost-benefits of each. Balikpapan is a large city with many highly valuable assets<br />
and thus a good target for more analysis; coastal flooding is also a clear threat. The first step will<br />
be to model the economic losses by creating granular spatial maps of Balikpapan’s residential<br />
and industrial assets and overlapping these with various coastal flooding scenarios. The long list<br />
of coastal flooding countermeasures would need to have their costs estimated and compared to<br />
their ability to reduce the negative impact of the flooding. The prioritized initiatives will be included<br />
Exhibit 72