East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
East Kalimantan Environmentally Sustainable Development Strategy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
107<br />
Proposed BFCP governance and management structure<br />
Funders<br />
▪ Bilateral<br />
▪ Multilateral<br />
▪ Philanthropic<br />
$$$<br />
$$$<br />
Buyers/<br />
investors<br />
ERs $$$<br />
BFCP<br />
trust<br />
SOURCE: The Nature Conservancy<br />
Other<br />
technical<br />
assistance<br />
(TNC, KfW)<br />
MRV<br />
to support governance and natural resource management. Communities adjacent to any BFCP<br />
site will be directly involved in the development and implementation of BFCP activities.<br />
Governance Case Study: Heart of Borneo<br />
In April 2005, delegations from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei Darussalam met to launch the<br />
Heart of Borneo Initiative. The three countries agreed to manage a cross-border area based on<br />
conservation and sustainable development principles. The Heart of Borneo covers around 22<br />
million hectares, and the largest portion (28 percent) in any province or state lies in <strong>East</strong> <strong>Kalimantan</strong><br />
with 6.1 million hectares of the total Heart of Borneo land area.<br />
DRAFT<br />
Given that the Heart of Borneo crosses not only districts and provinces but three countries, the<br />
project has developed a multi-layered governance structure that is a useful example (Table 3).<br />
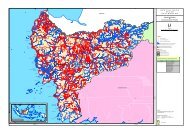
SPATIAL PLANNING AND POLICY<br />
Technical<br />
assistance and<br />
support unit<br />
Timber<br />
concessions<br />
Land use<br />
planning<br />
Supervisory council<br />
▪ District government<br />
▪ Provincial government<br />
▪ National government<br />
▪ Civil society/TNC<br />
Oil palm<br />
Secretariat<br />
REDD<br />
site<br />
activities<br />
Advisory<br />
group<br />
Joint<br />
working group<br />
Government<br />
institutions:<br />
District, province,<br />
national<br />
Governance<br />
and<br />
enforcement<br />
Protection<br />
forest<br />
Emissions reductions<br />
Stakeholder<br />
involvements<br />
Communities<br />
Given that the majority of <strong>East</strong> <strong>Kalimantan</strong>’s emissions are due to the conversion of forest and<br />
peatlands, the most critical regulatory issues are resolving land tenure and title disputes and<br />
optimizing land-use allocation through better spatial planning. Collaboration among national and<br />
district level governments will be critical due to the cross-jurisdictional nature of land tenure and<br />
spatial planning issues. In addition, any collaboration needs to be supported by detailed technical<br />
analyses, which can accurately assess current land allocation and the potential economic benefits<br />
of using land types for different activities. Box 10 discusses the current levels of spatial planning.<br />
Exhibit 74<br />
A single land titling system to register deeds and map land holdings is a necessary tool, and such a<br />
system does not currently exist. Technology offers ways to more cost- and time-efficiently build such<br />
a database. Indonesian planners recently built such a system in Aceh after the tsunami, overcoming