FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Dynamic DNS configurations<br />
Configuration overview<br />
Dynamic DNS configurations<br />
This section describes how to configure a site-to-site <strong>VPN</strong>, in which one <strong>FortiGate</strong><br />
unit has a static IP address and the other <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit has a static domain name<br />
and a dynamic IP address.<br />
The following topics are included in this section:<br />
• Configuration overview<br />
• General configuration steps<br />
• Configure the dynamically-addressed <strong>VPN</strong> peer<br />
• Configure the fixed-address <strong>VPN</strong> peer<br />
Configuration overview<br />
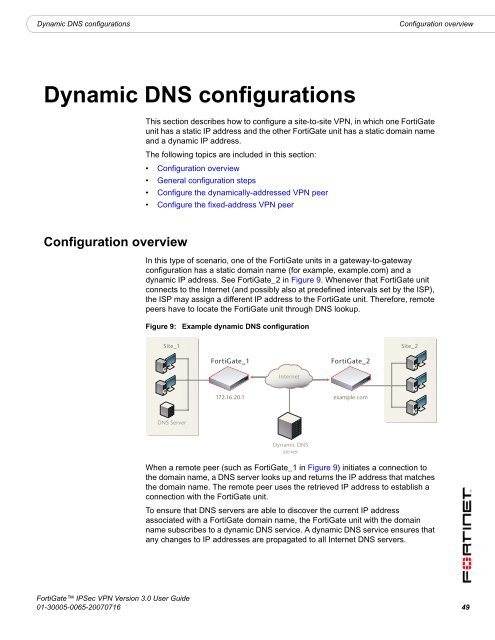
In this type of scenario, one of the <strong>FortiGate</strong> units in a gateway-to-gateway<br />
configuration has a static domain name (for example, example.<strong>com</strong>) and a<br />
dynamic IP address. See <strong>FortiGate</strong>_2 in Figure 9. Whenever that <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit<br />
connects to the Internet (and possibly also at predefined intervals set by the ISP),<br />
the ISP may assign a different IP address to the <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit. Therefore, remote<br />
peers have to locate the <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit through DNS lookup.<br />
Figure 9:<br />
Example dynamic DNS configuration<br />
Site_1<br />
Site_2<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong>_1<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong>_2<br />
Internet<br />
172.16.20.1<br />
example.<strong>com</strong><br />
DNS Server<br />
Dynamic DNS<br />
server<br />
When a remote peer (such as <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1 in Figure 9) initiates a connection to<br />
the domain name, a DNS server looks up and returns the IP address that matches<br />
the domain name. The remote peer uses the retrieved IP address to establish a<br />
connection with the <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit.<br />
To ensure that DNS servers are able to discover the current IP address<br />
associated with a <strong>FortiGate</strong> domain name, the <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit with the domain<br />
name subscribes to a dynamic DNS service. A dynamic DNS service ensures that<br />
any changes to IP addresses are propagated to all Internet DNS servers.<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong> <strong>IPSec</strong> <strong>VPN</strong> Version 3.0 <strong>User</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
01-30005-0065-20070716 49