FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide - FirewallShop.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Redundant <strong>VPN</strong> configurations<br />
Redundant route-based <strong>VPN</strong> configuration example<br />
Redundant route-based <strong>VPN</strong> configuration example<br />
This example demonstrates a fully redundant site-to-site <strong>VPN</strong> configuration using<br />
route-based <strong>VPN</strong>s. At each site, the <strong>FortiGate</strong> unit has two interfaces connected<br />
to the Internet through different ISPs. This means that there are four possible<br />
paths for <strong>com</strong>munication between the two units. In this example, these paths,<br />
listed in descending priority, are:<br />
• <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1 WAN 1 to <strong>FortiGate</strong>_2 WAN 1<br />
• <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1 WAN 1 to <strong>FortiGate</strong>_2 WAN 2<br />
• <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1 WAN 2 to <strong>FortiGate</strong>_2 WAN 1<br />
• <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1 WAN 2 to <strong>FortiGate</strong>_2 WAN 2<br />
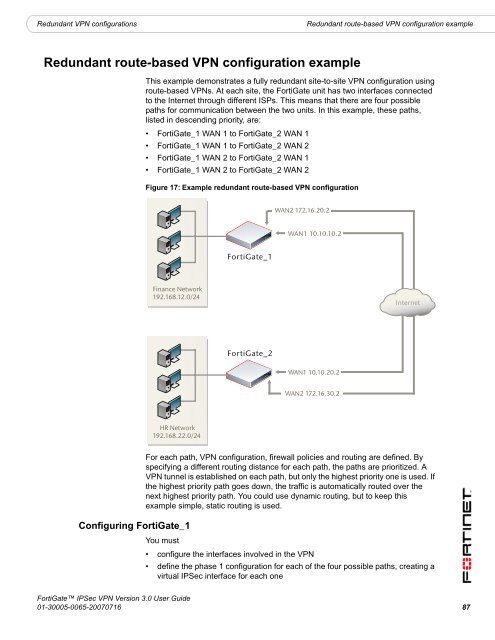
Figure 17: Example redundant route-based <strong>VPN</strong> configuration<br />
WAN2 172.16.20.2<br />
WAN1 10.10.10.2<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong>_1<br />
Finance Network<br />
192.168.12.0/24<br />
Internet<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong>_2<br />
WAN1 10.10.20.2<br />
WAN2 172.16.30.2<br />
HR Network<br />
192.168.22.0/24<br />
Configuring <strong>FortiGate</strong>_1<br />
For each path, <strong>VPN</strong> configuration, firewall policies and routing are defined. By<br />
specifying a different routing distance for each path, the paths are prioritized. A<br />
<strong>VPN</strong> tunnel is established on each path, but only the highest priority one is used. If<br />
the highest priority path goes down, the traffic is automatically routed over the<br />
next highest priority path. You could use dynamic routing, but to keep this<br />
example simple, static routing is used.<br />
You must<br />
• configure the interfaces involved in the <strong>VPN</strong><br />
• define the phase 1 configuration for each of the four possible paths, creating a<br />
virtual <strong>IPSec</strong> interface for each one<br />
<strong>FortiGate</strong> <strong>IPSec</strong> <strong>VPN</strong> Version 3.0 <strong>User</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
01-30005-0065-20070716 87