Resource Guide for Organic Insect and Disease ... - Cornell University
Resource Guide for Organic Insect and Disease ... - Cornell University
Resource Guide for Organic Insect and Disease ... - Cornell University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
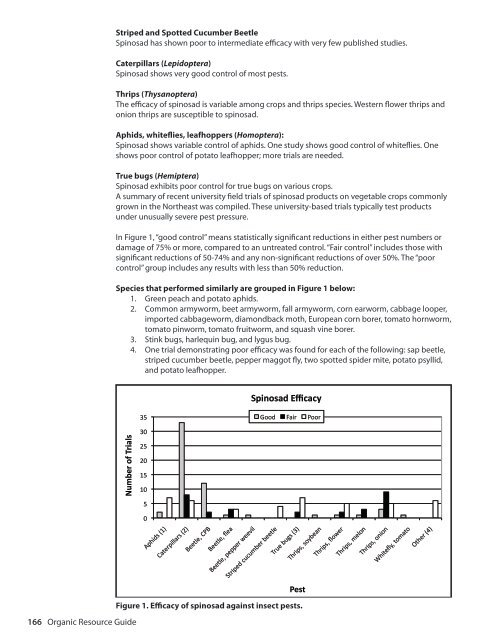
Striped <strong>and</strong> Spotted Cucumber Beetle<br />
Spinosad has shown poor to intermediate efficacy with very few published studies.<br />
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera)<br />
Spinosad shows very good control of most pests.<br />
Thrips (Thysanoptera)<br />
The efficacy of spinosad is variable among crops <strong>and</strong> thrips species. Western flower thrips <strong>and</strong><br />
onion thrips are susceptible to spinosad.<br />
Aphids, whiteflies, leafhoppers (Homoptera):<br />
Spinosad shows variable control of aphids. One study shows good control of whiteflies. One<br />
shows poor control of potato leafhopper; more trials are needed.<br />
True bugs (Hemiptera)<br />
Spinosad exhibits poor control <strong>for</strong> true bugs on various crops.<br />
A summary of recent university field trials of spinosad products on vegetable crops commonly<br />
grown in the Northeast was compiled. These university-based trials typically test products<br />
under unusually severe pest pressure.<br />
In Figure 1, “good control” means statistically significant reductions in either pest numbers or<br />
damage of 75% or more, compared to an untreated control. “Fair control” includes those with<br />
significant reductions of 50-74% <strong>and</strong> any non-significant reductions of over 50%. The “poor<br />
control” group includes any results with less than 50% reduction.<br />
Species that per<strong>for</strong>med similarly are grouped in Figure 1 below:<br />
1. Green peach <strong>and</strong> potato aphids.<br />
2. Common armyworm, beet armyworm, fall armyworm, corn earworm, cabbage looper,<br />
imported cabbageworm, diamondback moth, European corn borer, tomato hornworm,<br />
tomato pinworm, tomato fruitworm, <strong>and</strong> squash vine borer.<br />
3. Stink bugs, harlequin bug, <strong>and</strong> lygus bug.<br />
4. One trial demonstrating poor efficacy was found <strong>for</strong> each of the following: sap beetle,<br />
striped cucumber beetle, pepper maggot fly, two spotted spider mite, potato psyllid,<br />
<strong>and</strong> potato leafhopper.<br />
Spinosad Efficacy <br />
35 <br />
Good Fair Poor <br />
Number of Trials <br />
30 <br />
25 <br />
20 <br />
15 <br />
10 <br />
5 <br />
0 <br />
Aphids (1) <br />
Caterpillars (2) <br />
Beetle, CPB <br />
Beetle, flea <br />
Beetle, pepper weevil <br />
Striped cucumber beetle <br />
True bugs (3) <br />
Thrips, soybean <br />
Thrips, flower <br />
Thrips, melon <br />
Thrips, onion <br />
Whitefly, tomato <br />
Other (4) <br />
Pest <br />
166 <strong>Organic</strong> <strong>Resource</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
Figure 1. Efficacy of spinosad against insect pests.