Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
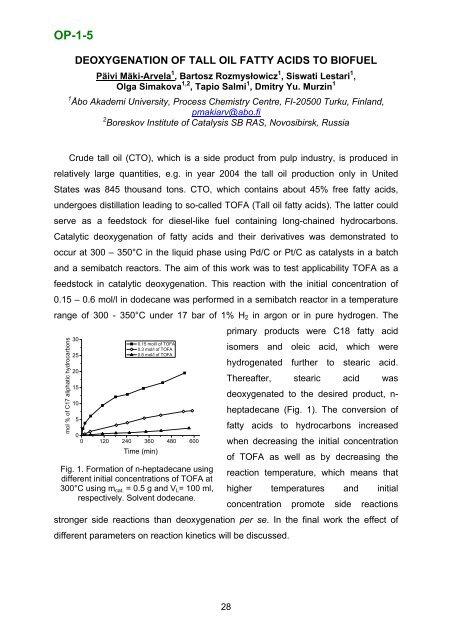
OP-1-5DEOXYGENATION OF TALL OIL FATTY ACIDS TO BIOFUELPäivi Mäki-Arvela 1 , Bartosz Rozmysłowicz 1 , Siswati Lestari 1 ,Olga Simakova 1,2 , Tapio Salmi 1 , Dmitry Yu. Murzin 11 Åbo Akademi University, Process Chemistry Centre, FI-20500 Turku, Finland,pmakiarv@abo.fi2 <strong>Boreskov</strong> <strong>Institute</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Catalysis</strong> <strong>SB</strong> <strong>RAS</strong>, <strong>Novosibirsk</strong>, <strong>Russia</strong>Crude tall oil (CTO), which is a side product from pulp industry, is produced inrelatively large quantities, e.g. in year 2004 the tall oil production only in UnitedStates was 845 thousand tons. CTO, which contains about 45% free fatty acids,undergoes distillation leading to so-called TOFA (Tall oil fatty acids). The latter couldserve as a feedstock for diesel-like fuel containing long-chained hydrocarbons.Catalytic deoxygenation <strong>of</strong> fatty acids and their derivatives was demonstrated tooccur at 300 – 350°C in the liquid phase using Pd/C or Pt/C as catalysts in a batchand a semibatch reactors. The aim <strong>of</strong> this work was to test applicability TOFA as afeedstock in catalytic deoxygenation. This reaction with the initial concentration <strong>of</strong>0.15 – 0.6 mol/l in dodecane was performed in a semibatch reactor in a temperaturerange <strong>of</strong> 300 - 350°C under 17 bar <strong>of</strong> 1% H 2 in argon or in pure hydrogen. Theprimary products were C18 fatty acid300.15 mol/l <strong>of</strong> TOFA0.3 mol/l <strong>of</strong> TOFA250.6 mol/l <strong>of</strong> TOFAisomers and oleic acid, which werehydrogenated further to stearic acid.20Thereafter, stearic acid was1510500 120 240 360 480 600deoxygenated to the desired product, n-heptadecane (Fig. 1). The conversion <strong>of</strong>fatty acids to hydrocarbons increasedwhen decreasing the initial concentrationTime (min)Fig. 1. Formation <strong>of</strong> n-heptadecane usingdifferent initial concentrations <strong>of</strong> TOFA at<strong>of</strong> TOFA as well as by decreasing thereaction temperature, which means that300°C using m cat. = 0.5 g and V L = 100 ml, higher temperatures and initialrespectively. Solvent dodecane.concentration promote side reactionsstronger side reactions than deoxygenation per se. In the final work the effect <strong>of</strong>different parameters on reaction kinetics will be discussed.mol % <strong>of</strong> C17 aliphatic hydrocarbons28