Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
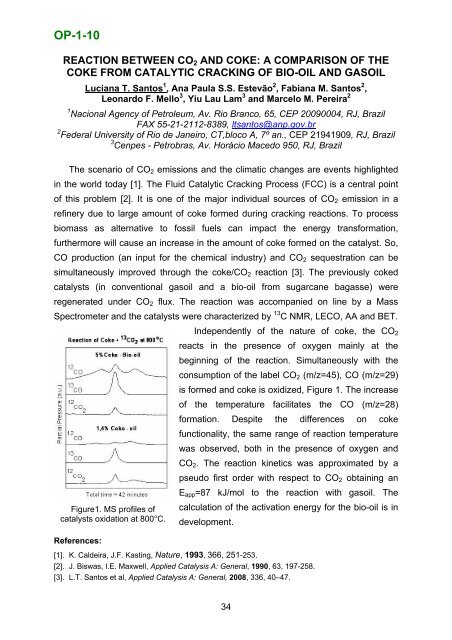
OP-1-10REACTION BETWEEN CO 2 AND COKE: A COMPARISON OF THECOKE FROM CATALYTIC CRACKING OF BIO-OIL AND GASOILLuciana T. Santos 1 , Ana Paula S.S. Estevão 2 , Fabiana M. Santos 2 ,Leonardo F. Mello 3 , Yiu Lau Lam 3 and Marcelo M. Pereira 21 Nacional Agency <strong>of</strong> Petroleum, Av. Rio Branco, 65, CEP 20090004, RJ, BrazilFAX 55-21-2112-8389, ltsantos@anp.gov.br2 Federal University <strong>of</strong> Rio de Janeiro, CT,bloco A, 7º an., CEP 21941909, RJ, Brazil3 Cenpes - Petrobras, Av. Horácio Macedo 950, RJ, BrazilThe scenario <strong>of</strong> CO 2 emissions and the climatic changes are events highlightedin the world today [1]. The Fluid Catalytic Cracking Process (FCC) is a central point<strong>of</strong> this problem [2]. It is one <strong>of</strong> the major individual sources <strong>of</strong> CO 2 emission in arefinery due to large amount <strong>of</strong> coke formed during cracking reactions. To processbiomass as alternative to fossil fuels can impact the energy transformation,furthermore will cause an increase in the amount <strong>of</strong> coke formed on the catalyst. So,CO production (an input for the chemical industry) and CO 2 sequestration can besimultaneously improved through the coke/CO 2 reaction [3]. The previously cokedcatalysts (in conventional gasoil and a bio-oil from sugarcane bagasse) wereregenerated under CO 2 flux. The reaction was accompanied on line by a MassSpectrometer and the catalysts were characterized by 13 C NMR, LECO, AA and BET.Independently <strong>of</strong> the nature <strong>of</strong> coke, the CO 2reacts in the presence <strong>of</strong> oxygen mainly at thebeginning <strong>of</strong> the reaction. Simultaneously with theconsumption <strong>of</strong> the label CO 2 (m/z=45), CO (m/z=29)is formed and coke is oxidized, Figure 1. The increase<strong>of</strong> the temperature facilitates the CO (m/z=28)formation. Despite the differences on cokefunctionality, the same range <strong>of</strong> reaction temperaturewas observed, both in the presence <strong>of</strong> oxygen andCO 2 . The reaction kinetics was approximated by apseudo first order with respect to CO 2 obtaining anE app =87 kJ/mol to the reaction with gasoil. TheFigure1. MS pr<strong>of</strong>iles <strong>of</strong>catalysts oxidation at 800°C.calculation <strong>of</strong> the activation energy for the bio-oil is indevelopment.References:[1]. K. Caldeira, J.F. Kasting, Nature, 1993, 366, 251-253.[2]. J. Biswas, I.E. Maxwell, Applied <strong>Catalysis</strong> A: General, 1990, 63, 197-258.[3]. L.T. Santos et al, Applied <strong>Catalysis</strong> A: General, 2008, 336, 40–47.34