Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
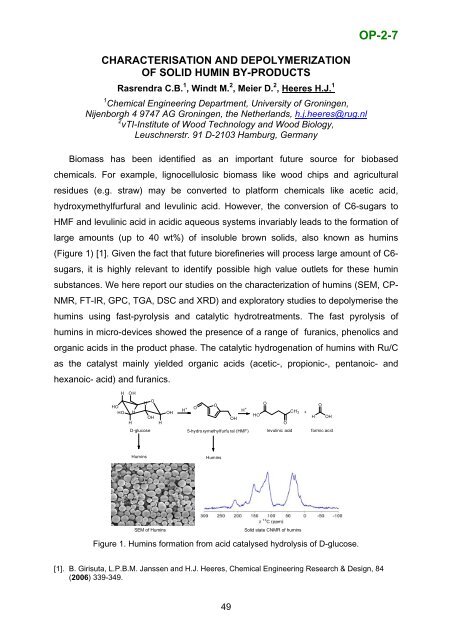
CHARACTERISATION AND DEPOLYMERIZATIONOF SOLID HUMIN BY-PRODUCTSRasrendra C.B. 1 , Windt M. 2 , Meier D. 2 , Heeres H.J. 11 Chemical Engineering Department, University <strong>of</strong> Groningen,Nijenborgh 4 9747 AG Groningen, the Netherlands, h.j.heeres@rug.nl2 vTI-<strong>Institute</strong> <strong>of</strong> Wood Technology and Wood Biology,Leuschnerstr. 91 D-2103 Hamburg, GermanyOP-2-7Biomass has been identified as an important future source for biobasedchemicals. For example, lignocellulosic biomass like wood chips and agriculturalresidues (e.g. straw) may be converted to platform chemicals like acetic acid,hydroxymethylfurfural and levulinic acid. However, the conversion <strong>of</strong> C6-sugars toHMF and levulinic acid in acidic aqueous systems invariably leads to the formation <strong>of</strong>large amounts (up to 40 wt%) <strong>of</strong> insoluble brown solids, also known as humins(Figure 1) [1]. Given the fact that future biorefineries will process large amount <strong>of</strong> C6-sugars, it is highly relevant to identify possible high value outlets for these huminsubstances. We here report our studies on the characterization <strong>of</strong> humins (SEM, CP-NMR, FT-IR, GPC, TGA, DSC and XRD) and exploratory studies to depolymerise thehumins using fast-pyrolysis and catalytic hydrotreatments. The fast pyrolysis <strong>of</strong>humins in micro-devices showed the presence <strong>of</strong> a range <strong>of</strong> furanics, phenolics andorganic acids in the product phase. The catalytic hydrogenation <strong>of</strong> humins with Ru/Cas the catalyst mainly yielded organic acids (acetic-, propionic-, pentanoic- andhexanoic- acid) and furanics.HHOHOOHHOOOOOHHOH+H +CH 3 +HOOHOHH OHHHOD-glucose 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) levulinic acid formic acidHuminsHuminsSEM <strong>of</strong> Humins Solid state CNMR <strong>of</strong> huminsFigure 1. Humins formation from acid catalysed hydrolysis <strong>of</strong> D-glucose.[1]. B. Girisuta, L.P.B.M. Janssen and H.J. Heeres, Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 84(2006) 339-349.49