SCHRIFTENREIHE Institut für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde ...
SCHRIFTENREIHE Institut für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde ...
SCHRIFTENREIHE Institut für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Table 9). In the topsoil layer, water repellency might be caused mainly by<br />
hydrophobic compo<strong>und</strong>s from decomposed soil organic matter (Piccolo and<br />
Mbagwu, 1999). Together with the initially existing heterogeneous distribution of<br />
various repellent substances, subsequent relocation and the transport along<br />
preferential flow paths might contribute to the spatial variability of WDPT and<br />
SWC.<br />
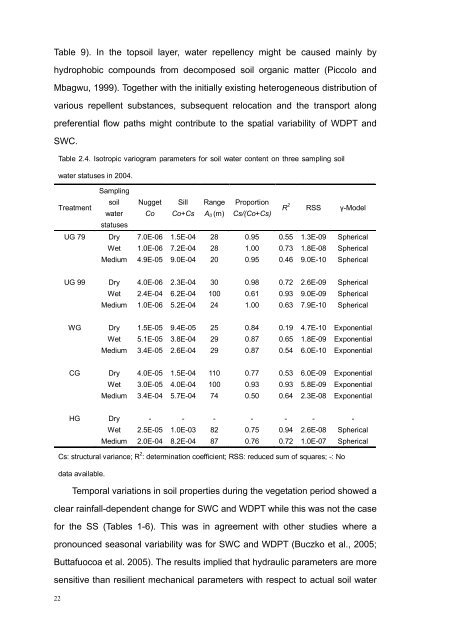
Table 2.4. Isotropic variogram parameters for soil water content on three sampling soil<br />
water statuses in 2004.<br />
Treatment<br />
Sampling<br />
soil<br />
water<br />
statuses<br />
Nugget<br />
Co<br />
Sill<br />
Co+Cs<br />
Range<br />
A0 (m)<br />
Proportion<br />
Cs/(Co+Cs)<br />
R 2 RSS γ-Model<br />
UG 79 Dry 7.0E-06 1.5E-04 28 0.95 0.55 1.3E-09 Spherical<br />
Wet 1.0E-06 7.2E-04 28 1.00 0.73 1.8E-08 Spherical<br />
Medium 4.9E-05 9.0E-04 20 0.95 0.46 9.0E-10 Spherical<br />
UG 99 Dry 4.0E-06 2.3E-04 30 0.98 0.72 2.6E-09 Spherical<br />
Wet 2.4E-04 6.2E-04 100 0.61 0.93 9.0E-09 Spherical<br />
Medium 1.0E-06 5.2E-04 24 1.00 0.63 7.9E-10 Spherical<br />
WG Dry 1.5E-05 9.4E-05 25 0.84 0.19 4.7E-10 Exponential<br />
Wet 5.1E-05 3.8E-04 29 0.87 0.65 1.8E-09 Exponential<br />
Medium 3.4E-05 2.6E-04 29 0.87 0.54 6.0E-10 Exponential<br />
CG Dry 4.0E-05 1.5E-04 110 0.77 0.53 6.0E-09 Exponential<br />
Wet 3.0E-05 4.0E-04 100 0.93 0.93 5.8E-09 Exponential<br />
Medium 3.4E-04 5.7E-04 74 0.50 0.64 2.3E-08 Exponential<br />
HG Dry - - - - - - -<br />
Wet 2.5E-05 1.0E-03 82 0.75 0.94 2.6E-08 Spherical<br />
Medium 2.0E-04 8.2E-04 87 0.76 0.72 1.0E-07 Spherical<br />
Cs: structural variance; R 2 : determination coefficient; RSS: reduced sum of squares; -: No<br />
data available.<br />
Temporal variations in soil properties during the vegetation period showed a<br />
clear rainfall-dependent change for SWC and WDPT while this was not the case<br />
for the SS (Tables 1-6). This was in agreement with other studies where a<br />
pronounced seasonal variability was for SWC and WDPT (Buczko et al., 2005;<br />
Buttafuocoa et al. 2005). The results implied that hydraulic parameters are more<br />
sensitive than resilient mechanical parameters with respect to actual soil water<br />
22